Table of Contents
ToggleUnderweight: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Homeopathic Medicines for Gain Weight and FAQs
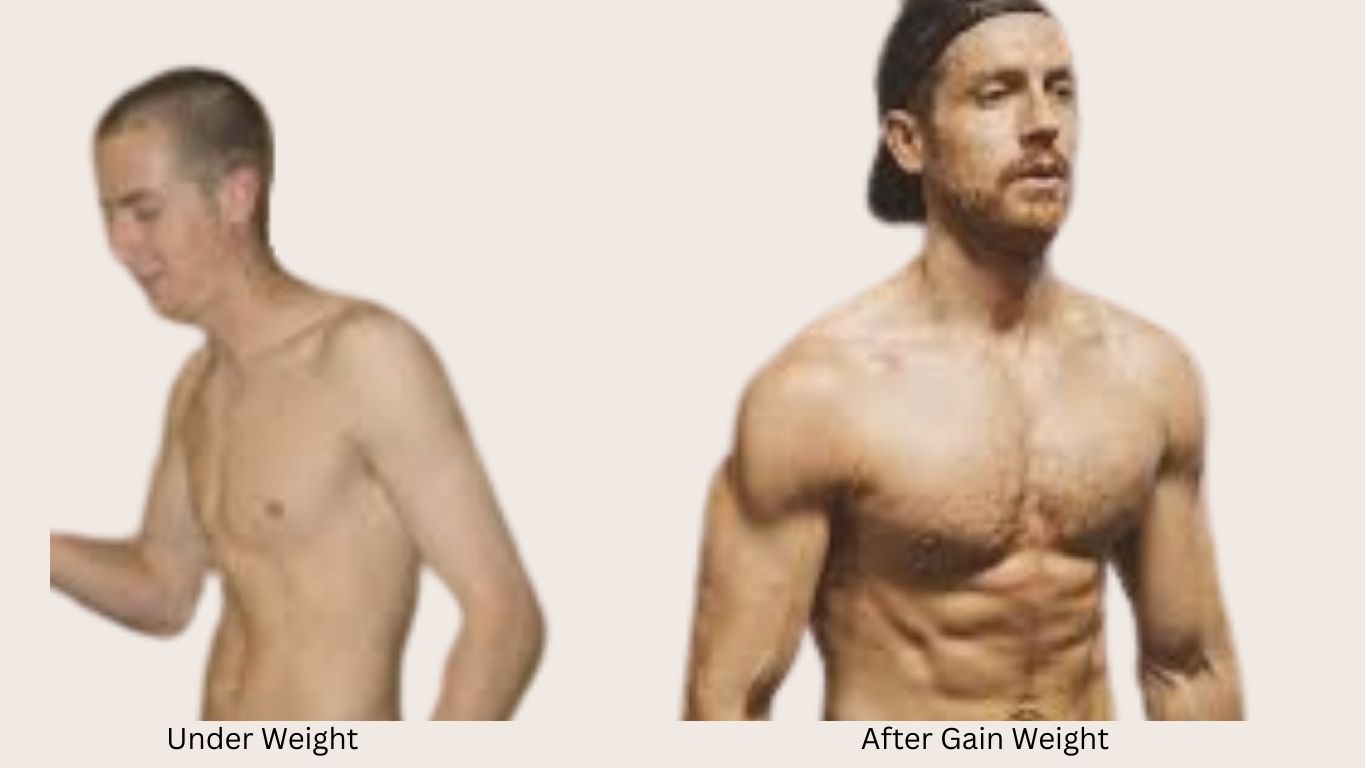
Introduction: The Overlooked Health Challenge
In a world preoccupied with obesity, the significant health condition of being underweight is frequently minimized or misunderstood. Classified by a Body Mass Index (BMI) below 18.5, it represents a state of nutritional deficit and physical vulnerability that extends far beyond a slender physique. For those affected, it is a daily reality of exhaustion, frequent illness, and systemic imbalance. This guide provides a comprehensive exploration of underweight status, detailing its recognizable symptoms, root causes, profound health effects, and strategies for healthy recovery, including an overview of the homeopathic approach.
Section 1: Recognizing the Symptoms
Being underweight manifests through a cluster of signs indicating the body lacks sufficient energy and nutrients for optimal function.
-
Persistent Fatigue and Low Energy: A profound, unshakable tiredness results from a caloric deficit, making routine tasks feel overwhelming.
-
Frequent Illness and Weak Immunity: Recurrent infections, slow healing, and prolonged recovery times signal a compromised immune system lacking essential proteins and vitamins.
-
Reproductive Disruption: In women, amenorrhea—the absence of menstrual periods—is a common sign as the body conserves energy by shutting down non-vital functions.
-
Cognitive and Physical Changes: “Brain fog,” poor concentration, and memory issues occur. Hair may thin and become brittle, while skin can appear dry, sallow, or flaky.
-
Temperature Dysregulation: A constant feeling of being cold, even in warm environments, points to insufficient insulating body fat and poor circulation.
-
Appetite Disturbance: A notably diminished appetite, where natural hunger cues are absent, further complicates nutritional intake.
-
Developmental Delays: In children, underweight status critically impacts growth rates, cognitive development, and puberty.
Section 2: Investigating the Root Causes
The etiology is complex, often involving an interplay of medical, psychological, and socioeconomic factors.
-
Underlying Medical Conditions:
-
Metabolic Disorders: Hyperthyroidism drastically increases metabolic rate.
-
Malabsorptive Diseases: Conditions like celiac disease, Crohn’s, and ulcerative colitis prevent nutrient absorption.
-
Chronic Illnesses: Cancer, COPD, HIV/AIDS, and uncontrolled diabetes increase metabolic demands and decrease appetite.
-
-
Psychological and Emotional Factors:
-
Eating Disorders: Anorexia nervosa and bulimia are severe mental health conditions central to weight loss.
-
Mental Health: Depression, anxiety, and chronic stress can suppress appetite and disrupt eating patterns.
-
-
Socioeconomic and Lifestyle Influences:
-
Food Insecurity: Poverty and lack of access to nutritious food is a primary global cause.
-
Occupational or Athletic Pressure: Certain sports or professions may culturally emphasize leanness.
-
Substance Use: Alcoholism and drug use severely disrupt metabolism and nutrition.
-
-
Constitutional Factors: A naturally fast metabolism or slender frame can be a predisposing factor, often activated by an additional trigger.
Section 3: Understanding the Long-Term Health Effects
Chronic underweight status leads to systemic deterioration as the body cannibalizes itself for energy.
-
Compromised Immunity: Increased susceptibility to persistent and severe infections.
-
Musculoskeletal Damage: Loss of muscle mass (sarcopenia), profound weakness, and decreased bone density (osteoporosis), elevating fracture risk.
-
Reproductive and Developmental Consequences: Infertility, higher risk of pregnancy complications, and significant developmental delays in children.
-
Nutritional Deficiencies: Iron-deficiency anemia, neurological issues from B12 deficiency, and electrolyte imbalances affecting heart function.
-
Psychological and Social Impact: Social stigma, anxiety, low self-esteem, and withdrawal due to constant commentary on body size.
Section 4: Strategies for Prevention and Healthy Weight Gain
Recovery focuses on sustainable nourishment and building strength through a gradual, multi-faceted approach.
-
Nutritional Rehabilitation:
-
Prioritize nutrient-dense, calorie-rich foods like nuts, seeds, avocados, full-fat dairy, lean meats, and whole grains.
-
Adopt smaller, frequent meals (5-6 daily) to overcome poor appetite.
-
Incorporate healthy high-calorie snacks such as trail mix, cheese, yogurt, and smoothies with nut butter.
-
-
Essential Lifestyle and Medical Support:
-
Mandatory Medical Evaluation: Rule out or treat underlying physiological causes first.
-
Strength Training: Resistance exercises (weight lifting, bands) are crucial to stimulate appetite and build lean muscle mass.
-
Professional Guidance: Consult a registered dietitian for a personalized plan and seek therapy (e.g., CBT) for eating disorders or associated anxiety/depression.
-
Section 5: Homeopathic Medicines for Gain Weight
Homeopathy offers a complementary, individualized system of medicine based on the principle of treating “like with like.” It aims to address the perceived underlying constitutional imbalance. This should only be pursued under the guidance of a qualified practitioner alongside conventional medical care.
A homeopath conducts an in-depth interview to select a remedy matching the individual’s unique physical, mental, and emotional symptom picture. Common remedies include:
-
Calcarea carbonica: For individuals who are fair, flabby, easily fatigued, anxious, and sweat easily, often with cravings for eggs.
-
Natrum muriaticum: Indicated after grief or emotional disappointment, where the person is reserved, craves salt, and worsens with consolation.
-
Iodum: For intense restlessness and warmth with a ravenous appetite yet progressive weight loss.
-
Abrotanum: Used for rapid wasting of strength, particularly in the legs, often following acute illness.
-
Silicea: For lean, frail individuals who are chilly, lack stamina, have weak digestion, and are prone to infections.
The goal is not merely to stimulate appetite but to address the holistic imbalance believed to hinder the body’s natural ability to maintain a healthy weight.
FAQs: Homeopathic Medicines for Gain Weight
1. What is the basic principle behind using homeopathy for weight gain?
Homeopathy operates on the principle of individualization and treating the “whole person.” It does not offer a single medicine like “weight gain pills.” Instead, a qualified homeopath selects a remedy based on your unique physical, mental, and emotional symptom picture, along with your body’s specific way of reacting to stress or illness. The goal is to correct the perceived underlying imbalance—which may involve metabolism, digestion, stress response, or nutrient absorption—that is preventing your body from reaching and maintaining its natural, healthy weight. The focus is on improving vitality and systemic function, which can lead to healthy weight gain as a secondary effect.
2. Are homeopathic medicines for weight gain safe and free from side effects?
Homeopathic medicines are prepared through a process of serial dilution and succussion (vigorous shaking). Due to their highly diluted nature, they are generally considered safe with a very low risk of direct side effects when taken as directed by a professional. They are non-habit forming. However, a “proving” can occur if an incorrect remedy is taken repeatedly, where symptoms similar to the medicine may appear temporarily. It is also crucial to understand that homeopathy is a complementary approach. Safety depends on first ruling out serious underlying medical conditions (like hyperthyroidism, diabetes, or eating disorders) with a conventional doctor. Homeopathy should not delay necessary medical diagnosis or treatment.
3. How long does it take to see results with homeopathic treatment for being underweight?
The timeline is highly individual and depends on the nature and duration of the problem. In acute cases of recent weight loss due to a short-term illness or grief, improvement can be relatively quicker, potentially within weeks. For chronic conditions where low weight has been a longstanding issue (often years), the treatment is also a longer-term process. It may take several months of consistent treatment with periodic follow-ups and potential remedy adjustments to observe steady, sustainable progress. Patience and consistency are key, as the aim is a gradual restoration of balance, not rapid weight gain.
4. Can I take homeopathic medicines along with my regular allopathic (conventional) medicines?
Generally, yes. Homeopathic medicines are usually compatible with conventional medications. They work on a different paradigm and are not known to interfere chemically with allopathic drugs. However, it is absolutely essential to inform both your homeopath and your medical doctor about all the treatments and medications you are using. This ensures coordinated care and allows your practitioners to monitor your overall health effectively. Never discontinue prescribed conventional medication without consulting your doctor.
5. Do I need to follow a special diet while taking homeopathic medicines for weight gain?
While there is no universal restrictive diet, a homeopath will likely emphasize the importance of a nutrient-dense, calorie-rich diet to support the body’s healing process. They may provide general nutritional guidance tailored to your needs. The classical homeopathic advice to avoid strong-smelling substances like coffee, menthol (in some toothpastes/candies), and camphor is often given, as these are believed by some practitioners to potentially interfere with the action of the remedy. Your homeopath will give you specific instructions based on the remedy prescribed.
6. What are some commonly prescribed homeopathic medicines for weight-related issues, and can I self-prescribe?
Commonly indicated remedies include:
-
Calcarea carbonica: For individuals who tire easily, feel anxious, sweat on the head, and may crave eggs and indigestible things.
-
Natrum muriaticum: For weight loss after grief or emotional upset, where the person is reserved, thirstless, and craves salt.
-
Iodum: For a ravenous appetite with progressive weight loss, accompanied by restlessness, heat intolerance, and a constant need for activity.
-
Silicea: For lean, frail individuals who are chilly, lack stamina, have weak digestion, and are prone to infections.
Self-prescription is strongly discouraged. These are examples, and the correct remedy choice depends on a deep, professional understanding of your complete symptom profile. Taking the wrong remedy will be ineffective at best and could temporarily aggravate symptoms.
7. Can homeopathy help with weight gain caused by an eating disorder like anorexia?
Homeopathy can play a supportive role in a comprehensive treatment plan for eating disorders, but it must never be the sole or primary treatment. Eating disorders are serious, potentially life-threatening mental health conditions that require a specialized multidisciplinary team, including a medical doctor, psychiatrist, psychotherapist, and registered dietitian. A homeopath can work alongside this team, focusing on addressing underlying anxiety, obsessive thoughts, or the physical effects of malnutrition, while the core psychological work is handled by mental health specialists.
8. Will the weight gained through homeopathic treatment be healthy muscle, or just fat?
The objective of constitutional homeopathic treatment is to improve the overall function of the body’s systems, including digestion and metabolism. When combined with proper nutrition and, importantly, appropriate strength-training or resistance exercises, the body is more likely to build lean muscle mass. Homeopathy aims to restore the body’s ability to utilize nutrients effectively. Therefore, the resulting weight gain, when achieved as part of a holistic plan involving diet and exercise, should contribute to a healthier, more resilient body composition rather than just accumulating fat.
Conclusion: A Path to Holistic Recovery
Addressing underweight status is a journey toward restoring vitality, not just adding pounds. It requires compassion, a thorough investigation into causative factors, and a sustained commitment to nourishing the body and mind. Successful management integrates sound medical diagnosis, strategic nutritional support, psychological care, and, where chosen, complementary holistic practices. True health is achieved not by reaching a specific number on the scale, but by fostering a state of complete physical resilience, mental well-being, and energetic balance.
6 thoughts on “Homeopathic Medicines for Gain Weight”