Homeopathic Remedies for Postpartum Hemorrhage: A comprehensive guide that delves into the use of homeopathic treatments to address postpartum hemorrhage.
Introduction
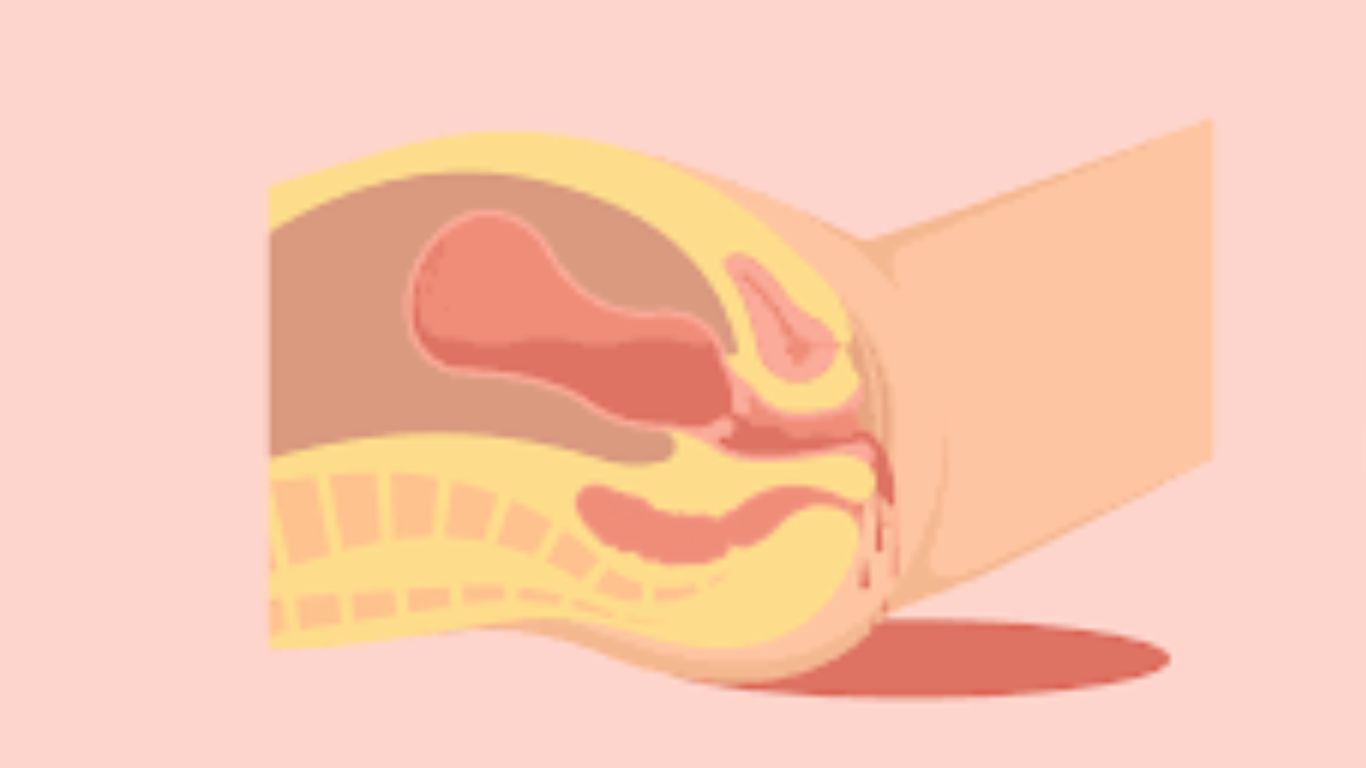
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is one of the most serious and frightening complications that can occur after childbirth. It refers to excessive bleeding following the birth of a baby and is a leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide, particularly in low-resource settings. Understanding PPH, its symptoms, causes, effects, prevention strategies, and treatment options, including homeopathic remedies, is crucial for ensuring the health and safety of new mothers.
What is Postpartum Hemorrhage?
Postpartum hemorrhage is defined as the loss of more than 500 milliliters of blood after vaginal delivery or more than 1,000 milliliters after a cesarean section. While some bleeding after delivery is normal, PPH involves excessive blood loss that can threaten a mother’s life if not managed promptly. PPH can occur immediately after birth (primary PPH) or between 24 hours and 12 weeks postpartum (secondary PPH).
Symptoms of Postpartum Hemorrhage
Recognizing the symptoms of PPH is essential for immediate action and treatment. Symptoms may vary in intensity, but common signs include:
- Excessive Vaginal Bleeding: Continuous or heavy bleeding that does not slow down, often bright red.
- Low Blood Pressure: Blood pressure may drop rapidly, causing dizziness and fainting.
- Rapid Heart Rate: The heart may beat faster than usual as the body attempts to compensate for blood loss.
- Pale, Cold, and Clammy Skin: Reduced blood flow to the skin can cause a pale and cold appearance.
- Weakness and Fatigue: Severe blood loss leads to extreme fatigue and a feeling of weakness.
- Swelling and Pain in the Lower Abdomen: The uterus may feel tender and enlarged due to retained blood or clots.
- Confusion or Disorientation: Severe blood loss can impair brain function, leading to confusion.
- Decreased Urine Output: Reduced blood flow to the kidneys can cause a drop in urine production.
Causes of Postpartum Hemorrhage
Several factors can contribute to PPH, and understanding these causes helps in prevention and management:
- Uterine Atony: This is the most common cause of PPH, where the uterus fails to contract adequately after delivery, resulting in continued bleeding.
- Retained Placental Tissue: If parts of the placenta or membranes remain in the uterus, they can prevent the uterus from contracting properly.
- Trauma to the Birth Canal: Tears or lacerations in the uterus, cervix, or vagina during delivery can lead to significant blood loss.
- Coagulation Disorders: Conditions that affect the blood’s ability to clot, such as pre-existing bleeding disorders or complications like disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
- Uterine Rupture: Rare but serious, this occurs when the uterus tears during labor, usually in women with a previous cesarean section scar.
- Placenta Accreta: A condition where the placenta abnormally attaches too deeply into the uterine wall, making it difficult to detach after delivery.
- Prolonged Labor or Rapid Delivery: Both prolonged and extremely rapid labors can increase the risk of PPH.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Women carrying twins or multiples have a higher risk due to the increased size of the uterus and higher blood supply needs.
- Use of Medications: Certain medications used during labor, such as oxytocin or magnesium sulfate, can influence uterine contractions and bleeding.
Effects of Postpartum Hemorrhage
PPH can have profound physical and emotional effects on new mothers, ranging from immediate health risks to long-term consequences:
- Anemia: Significant blood loss can lead to anemia, causing prolonged fatigue, weakness, and reduced ability to care for the newborn.
- Hypovolemic Shock: Severe blood loss can lead to shock, a life-threatening condition where vital organs do not receive enough blood.
- Organ Failure: In extreme cases, insufficient blood flow can cause failure of critical organs, such as the kidneys, liver, or heart.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Blood loss can compromise the immune system, making the mother more susceptible to postpartum infections.
- Emotional and Psychological Impact: The trauma of experiencing PPH can lead to anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), affecting the overall postpartum experience.
- Extended Hospital Stay: Mothers with PPH often require additional monitoring, blood transfusions, or surgical interventions, resulting in longer hospital stays.
- Impact on Breastfeeding: Anemia and the physical toll of PPH can affect milk supply and breastfeeding ability.
- Future Pregnancy Risks: Women who have experienced PPH are at a higher risk of recurrence in future pregnancies, necessitating more vigilant prenatal care.
Prevention of Postpartum Hemorrhage
Preventing PPH involves a combination of proactive management strategies during pregnancy, labor, and the postpartum period:
- Regular Prenatal Care: Regular check-ups during pregnancy help identify risk factors, such as anemia or clotting disorders, that can be managed ahead of delivery.
- Active Management of the Third Stage of Labor: This includes administering uterotonic medications immediately after birth to encourage uterine contraction and reduce bleeding.
- Controlled Cord Traction: Proper technique during the delivery of the placenta helps prevent uterine inversion or retained placental tissue.
- Adequate Nutrition: Ensuring a balanced diet with sufficient iron and vitamin levels helps maintain healthy blood volume and clotting function.
- Monitoring High-Risk Pregnancies: Women with known risk factors, such as previous PPH, should be closely monitored and have a clear birth plan in place.
- Avoid Excessive Interventions: Limiting unnecessary interventions during labor, such as multiple vaginal exams or prolonged use of certain medications, can reduce trauma to the birth canal.
- Training and Preparedness of Healthcare Staff: Ensuring that healthcare providers are trained to recognize and manage PPH promptly can significantly reduce maternal morbidity and mortality.
Homeopathic Remedies for Postpartum Hemorrhage
Homeopathy offers gentle, natural remedies that can support the body’s healing process during PPH. While homeopathic treatment should always be used in conjunction with medical care in emergencies, it can be beneficial as a complementary approach.
- Sabina: This remedy is particularly effective for bright red, gushing blood with clots, often accompanied by severe pain that radiates to the lower back and thighs. It is commonly used when there is heavy bleeding with a history of miscarriage or retained placenta.
- Secale Cornutum: Used in cases where the blood is dark, thin, and continuous, Secale Cornutum is suitable for weak uterine contractions and when the uterus feels relaxed. It is especially helpful for women who feel cold and have a pale appearance.
- Cinchona (China): Cinchona is highly effective for managing the aftermath of blood loss, particularly when the patient feels exhausted, weak, and faint. It helps restore energy levels and supports recovery from anemia.
- Ipecacuanha: This remedy is indicated when there is persistent bleeding with nausea, faintness, and lack of uterine contraction. The blood is often bright red, and the patient may feel chilly or cold despite the heavy bleeding.
- Belladonna: Suitable for cases where there is sudden, profuse bleeding with a sensation of heat and throbbing pain in the uterus. Belladonna is ideal for women who are flushed, agitated, and have a rapid pulse.
- Trillium Pendulum: Known for managing bleeding that feels as though the hips are being pulled apart, Trillium is effective for uterine atony with bright red blood and weakness. It is often used when bleeding worsens with movement.
- Arnica Montana: Arnica is beneficial for cases of hemorrhage due to trauma during delivery. It helps reduce bruising, control bleeding, and supports overall healing of the uterus and surrounding tissues.
- Erigeron: This remedy is used for bright red hemorrhages that occur with frequent urination and a feeling of pressure in the pelvic region. It is particularly helpful for secondary PPH that occurs days or weeks after delivery.
- Phosphorus: Phosphorus is indicated for bright red, gushing blood that is not easily controlled. It is especially useful when bleeding is accompanied by anxiety, palpitations, and a strong desire for cold drinks.
Case Study: A Personal Journey with PPH
To illustrate the impact of PPH, let’s look at the story of Sarah, a new mother who experienced severe postpartum hemorrhage after the birth of her first child. Sarah’s labor was long and difficult, and after her baby was born, she began to feel light-headed and noticed that the bleeding was not stopping. Her healthcare team quickly intervened, administering medications to help her uterus contract and stopping the bleeding. Although she required a blood transfusion, Sarah’s recovery was supported by homeopathic remedies, including Cinchona to help rebuild her strength and Arnica to manage the trauma and bruising.
The emotional toll of PPH was significant for Sarah, who felt anxious about her health and ability to care for her newborn. With the support of her family, healthcare providers, and a homeopath, Sarah gradually regained her strength. Her experience highlights the importance of a well-prepared birth plan, knowledgeable medical staff, and the supportive role of homeopathic remedies in postpartum recovery.
FAQs: Homeopathic Medicines for Postpartum Hemorrhage
- What is postpartum hemorrhage and how can homeopathy help?
Postpartum hemorrhage refers to excessive bleeding after childbirth. Homeopathy can help manage this condition by using remedies to address the underlying causes of the bleeding and support the body’s natural healing processes. Homeopathic remedies aim to reduce bleeding, alleviate associated symptoms, and restore balance to the body’s systems.
- What are common homeopathic remedies for postpartum hemorrhage?
Common homeopathic remedies for postpartum hemorrhage include:
- China (Cinchona officinalis): Used for excessive bleeding with weakness, fatigue, and a feeling of emptiness.
- Kali Carb (Kali Carbonicum): Helpful for profuse bleeding with a sensation of heaviness or pressure.
- Belladonna: Effective for sudden, intense bleeding with symptoms of heat, redness, and throbbing.
- Hamamelis (Witch Hazel): Used for bleeding with a tendency to form clots and a feeling of soreness.
- How do these homeopathic remedies work for postpartum hemorrhage?
Homeopathic remedies work by stimulating the body’s natural healing processes and addressing the specific symptoms associated with postpartum hemorrhage. Each remedy is selected based on the individual’s symptoms, such as the nature of the bleeding, accompanying sensations, and overall physical condition. The goal is to restore balance and promote recovery.
- How does a homeopath determine the appropriate remedy for postpartum hemorrhage?
A homeopath determines the appropriate remedy by conducting a thorough assessment of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and overall health. This includes evaluating the characteristics of the bleeding (e.g., quantity, color, and consistency), as well as any accompanying symptoms and the patient’s overall state. The remedy is chosen based on how well it matches the individual’s overall picture.
- Are homeopathic remedies safe for women experiencing postpartum hemorrhage?
Homeopathic remedies are generally considered safe for women experiencing postpartum hemorrhage, as they are highly diluted and have a low risk of side effects. However, it is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare provider or homeopath to ensure the remedies are appropriate for the specific condition and do not interfere with other treatments or medications.
- Can homeopathy be used alongside conventional treatments for postpartum hemorrhage?
Yes, homeopathy can be used alongside conventional treatments for postpartum hemorrhage. It is important to inform both your homeopath and conventional healthcare providers about all treatments being used to ensure they complement each other and do not cause interactions. Homeopathy can be a supportive therapy that enhances overall recovery and well-being.
- How long does it typically take to see results from homeopathic treatment for postpartum hemorrhage?
The time required to see results from homeopathic treatment can vary depending on the severity of the hemorrhage, the individual’s overall health, and how well the remedy matches the symptoms. Some women may notice improvements within a few days, while others may take longer. Regular follow-ups with the homeopath can help monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
- Can homeopathic remedies help prevent postpartum hemorrhage?
Homeopathic remedies are primarily used to treat existing conditions rather than prevent them. However, a homeopath may provide recommendations for remedies or lifestyle adjustments that support overall health and potentially reduce the risk of complications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and receiving proper prenatal care are also important for preventing postpartum hemorrhage.
- Are there any lifestyle changes that can complement homeopathic treatment for postpartum hemorrhage?
Lifestyle changes that can complement homeopathic treatment for postpartum hemorrhage include:
- Maintaining a balanced diet: Eating nutritious foods that support overall health and recovery.
- Staying hydrated: Ensuring adequate fluid intake to support bodily functions and healing.
- Resting adequately: Getting sufficient rest to help the body recover from childbirth.
- Monitoring for signs of complications: Being aware of any changes in bleeding or other symptoms and seeking medical attention if needed.
- When should a woman seek conventional medical help in addition to homeopathic treatment for postpartum hemorrhage?
A woman should seek conventional medical help in addition to homeopathic treatment if she experiences severe or persistent bleeding, signs of infection (such as fever or chills), significant pain, or any other concerning symptoms. Prompt medical attention is essential to ensure appropriate management and prevent complications. Combining homeopathy with conventional care can provide a comprehensive approach to recovery and well-being.
Conclusion
Postpartum hemorrhage is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate attention and effective management. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and effects of PPH, mothers and healthcare providers can work together to prevent and treat this condition. Homeopathic medicines offer a gentle and supportive approach that can complement conventional medical care, helping new mothers recover more fully and confidently after childbirth. As always, any treatment, including homeopathy, should be tailored to the individual and used under the guidance of qualified professionals to ensure the best outcomes for maternal health.
2 thoughts on “Homeopathic Remedies for Postpartum Hemorrhage”