Title: Understanding Cat Scratch Disease: Symptoms,
Causes, Effects, Prevention, and Homeopathic Medicines for Cat Scratch Disease
Introduction:
Cat scratch disease (CSD), also known as cat scratch fever,
is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Bartonella henselae. While
usually mild, CSD can cause discomfort and complications, particularly in
individuals with weakened immune systems. Understanding the symptoms,
identifying the causes, implementing preventive measures, and exploring
treatment options, including homeopathic remedies, are essential for managing
cat scratch disease effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into
the intricacies of cat scratch disease, providing insights into its symptoms,
causes, effects, prevention strategies, and the role of homeopathic treatment
in promoting healing and recovery.
Cat Scratch Disease: Symptoms
The symptoms of cat scratch disease can vary depending on
the individual’s immune response, the severity of the infection, and the
presence of underlying health conditions. Common symptoms may include:
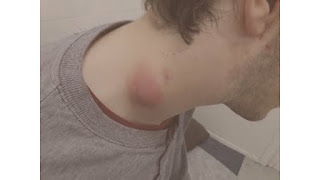
- Skin
Lesions: The primary symptom of cat scratch disease is a small, raised
bump or pustule at the site of the cat scratch or bite. This lesion may
appear within 3-14 days after exposure and can be accompanied by redness,
swelling, and tenderness. - Lymph
Node Swelling: One of the hallmark symptoms of cat scratch disease is
swelling of the lymph nodes near the site of the scratch or bite. The
lymph nodes may become enlarged, tender, and painful to the touch. Swollen
lymph nodes are typically located in the armpit, neck, or groin area. - Fever:
Some individuals with cat scratch disease may develop a low-grade fever,
usually less than 102°F (38.9°C). Fever is a sign of the body’s immune
response to the bacterial infection and may be accompanied by chills,
sweats, and fatigue. - Malaise:
Cat scratch disease can cause general feelings of malaise, fatigue, and
discomfort. Individuals may experience a lack of energy, weakness, and a
sense of overall unwellness. - Headache:
Some individuals with cat scratch disease may experience mild to moderate
headaches, particularly if fever is present. Headaches may be accompanied
by other flu-like symptoms such as muscle aches and joint pain. - Loss
of Appetite: Cat scratch disease can cause a temporary loss of
appetite or decreased interest in food. Individuals may experience nausea,
vomiting, or abdominal discomfort, although these symptoms are less
common.
Causes of Cat Scratch Disease:
Cat scratch disease is caused by the bacterium Bartonella
henselae, which is primarily carried by cats, particularly kittens. The
bacterium is transmitted to humans through scratches, bites, or saliva from
infected cats. The primary causes of cat scratch disease include:
- Cat
Scratches or Bites: Cat scratch disease is most commonly transmitted
to humans through scratches or bites from infected cats. The bacterium
Bartonella henselae is present in the saliva, fur, and claws of infected
cats and can be introduced into the human body through breaks in the skin. - Kitten
Scratches: Kittens are more likely to carry and transmit Bartonella
henselae than adult cats. Young kittens may be infected with the bacterium
through exposure to fleas, which serve as vectors for transmission.
Kittens may exhibit playful behavior that includes scratching or biting,
increasing the risk of transmission to humans. - Flea
Infestation: Fleas play a role in the transmission of Bartonella
henselae between cats and may indirectly contribute to the spread of cat
scratch disease to humans. Infected fleas can bite cats, transmit the
bacterium, and then bite humans, introducing the bacterium into the
bloodstream through flea saliva. - Cat
Grooming Behavior: Cats groom themselves by licking their fur, which
can spread the bacterium Bartonella henselae throughout their coat.
Individuals may become exposed to the bacterium by petting or handling an
infected cat, particularly if they have open wounds or mucous membranes
that come into contact with contaminated fur or saliva. - Immune
Response: The severity of cat scratch disease in humans may be
influenced by the individual’s immune response to the bacterial infection.
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as young children, elderly
adults, or individuals with underlying health conditions, may be more
susceptible to complications from cat scratch disease.
Effects of Cat Scratch Disease:
Cat scratch disease is typically a self-limiting illness
that resolves on its own without specific treatment. However, in some cases,
the infection can lead to complications, particularly in individuals with
weakened immune systems. The effects of cat scratch disease may include:
- Lymphadenopathy:
Swollen lymph nodes, or lymphadenopathy, is a common complication of cat
scratch disease. The lymph nodes near the site of the scratch or bite may
become enlarged, tender, and painful. In severe cases, lymphadenopathy may
persist for several weeks or months and require medical evaluation. - Abscess
Formation: Rarely, cat scratch disease can lead to the formation of
abscesses, or collections of pus, at the site of the scratch or bite.
Abscesses may develop if the bacterial infection spreads beyond the lymph
nodes into surrounding tissues. Abscesses may require drainage and
antibiotic treatment to resolve. - Systemic
Symptoms: In severe cases of cat scratch disease, individuals may
experience systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, sweats, headache, and
fatigue. Systemic symptoms may indicate a more widespread infection or
complications requiring medical intervention. - Parinaud’s
Oculoglandular Syndrome: Parinaud’s oculoglandular syndrome is rare
complication of cat scratch disease characterized by inflammation of the
eye (conjunctivitis) and nearby lymph nodes. Individuals may experience
redness, swelling, and discharge from the affected eye, along with fever
and swollen lymph nodes. - Neurological
Complications: In rare cases, cat scratch disease may lead to
neurological complications such as encephalitis, meningitis, or seizures.
Neurological symptoms may occur due to inflammation of the brain or spinal
cord caused by the bacterial infection. - Disseminated
Infection: Immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS
or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, may be at risk of disseminated
cat scratch disease, where the infection spreads to other organs or
tissues. Disseminated infection may result in more severe symptoms and
require aggressive medical management.
Prevention of Cat Scratch Disease:
Preventing cat scratch disease involves minimizing the risk
of exposure to Bartonella henselae and practicing good hygiene and pet care
practices. Here are some key strategies for preventing cat scratch disease:
- Avoid
Rough Play: Avoid rough play with cats, particularly kittens, to
reduce the risk of scratches or bites that can transmit Bartonella
henselae. Teach children how to handle cats gently and avoid provoking
aggressive behavior. - Regular
Veterinary Care: Ensure that cats receive regular veterinary
check-ups, vaccinations, and flea control to maintain their health and
reduce the risk of infection with Bartonella henselae. Discuss preventive
measures and parasite control with your veterinarian. - Flea
Control: Keep cats and their environment free from fleas by using
veterinary-approved flea control products, regular grooming, and
environmental management. Flea control is essential for preventing
flea-borne transmission of Bartonella henselae between cats and humans. - Hand
Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling
cats, particularly after playing or grooming activities. Avoid touching
your face, mouth, or eyes with unwashed hands to prevent the introduction
of bacteria into mucous membranes. - Cat
Scratch Management: Trim cats’ claws regularly to minimize the risk of
deep scratches that can introduce bacteria into the skin. If scratched or
bitten by a cat, clean the wound with soap and water, apply an antiseptic,
and seek medical attention if necessary, especially if the wound appears
deep or becomes infected. - Education
and Awareness: Educate family members, especially children, about the
risks of cat scratch disease and proper pet care practices. Teach children
how to interact safely with cats, recognize signs of aggression or
discomfort and respond appropriately to scratches or bites.
Homeopathic Medicines for Cat Scratch Disease:
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing cat
scratch disease, focusing on stimulating the body’s natural healing mechanisms
and restoring balance. While homeopathic remedies cannot directly kill the
bacterium Bartonella henselae, they may help alleviate symptoms, support immune
function, and promote overall recovery. Here are some common homeopathic
remedies that may be used in the treatment of cat scratch disease:
- Apis
mellifica: Apis mellifica is indicated for swollen, hot, and painful
lymph nodes, especially when accompanied by stinging or burning
sensations. It may help reduce inflammation, relieve discomfort, and
promote drainage of swollen glands. - Belladonna:
Belladonna is indicated for sudden onset of symptoms, fever, redness, and
throbbing pain. It may help alleviate acute inflammation, feverish states,
and sensitivity to touch or light. - Hepar
sulphuris calcareum: Hepar sulphuris calcareum is indicated for
suppurative infections, abscess formation, and sensitivity to touch. It
may help promote suppuration, drain pus from abscesses, and accelerate the
healing process. - Silicea:
Silicea is indicated for slow-healing wounds, chronic infections, and
weakened immune systems. It may help support the body’s natural defenses,
enhance immune function, and facilitate the expulsion of foreign bodies or
toxins. - Calendula
officinalis: Calendula officinalis is indicated for wound healing,
skin infections, and inflammation. It may help promote tissue repair,
reduce swelling, and prevent secondary infections in scratched or injured
skin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Homeopathic
Medicine for Cat Scratch Disease:
- What
is homeopathic medicine, and how does it work for treating cat scratch
disease? Homeopathic medicine is a natural healing approach that
utilizes highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s innate healing
abilities. Homeopathic remedies for cat scratch disease aim to address the
symptoms associated with the illness, such as swollen lymph nodes, fever,
and discomfort, while supporting the body’s overall healing process. - Are
homeopathic remedies effective for treating cat scratch disease?
Homeopathic remedies can be part of a comprehensive treatment plan for cat
scratch disease, but their effectiveness may vary depending on factors
such as the severity of symptoms and the individual’s response to
treatment. While homeopathy cannot directly kill the bacterium Bartonella
henselae, it may help alleviate symptoms and promote overall recovery. - How
are homeopathic remedies administered to individuals with cat scratch
disease? Homeopathic remedies for cat scratch disease are typically
administered orally in the form of small pellets or liquid solutions. They
can be taken directly by mouth or dissolved in water. The frequency and
dosage of the remedy may vary depending on the individual’s symptoms,
response to treatment, and the guidance of a qualified homeopathic
practitioner. - Can
homeopathic treatment prevents cat scratch disease? Homeopathic
remedies cannot prevent cat scratch disease outright, but they may help
support the body’s immune response and overall health, reducing the
severity of symptoms and promoting faster recovery in the event of
infection. However, the most effective means of preventing cat scratch
disease is through practicing good hygiene, pet care, and cat behavior
management. - Are
there any side effects or risks associated with using homeopathic remedies
for cat scratch disease? Homeopathic remedies are generally considered
safe for use in individuals with cat scratch disease when administered
correctly and under the guidance of a qualified homeopathic practitioner.
They are non-toxic, gentle, and typically have minimal side effects
compared to conventional medications. However, individuals may react
differently to homeopathic remedies, and there is always a risk of adverse
reactions or interactions with other treatments. - Can
homeopathic treatment be used alongside conventional medical treatment for
cat scratch disease? Homeopathic treatment can complement conventional
medical treatment for cat scratch disease, but it should not replace
medical care or antibiotics, if necessary, especially in cases of severe
infection or complications. Individuals should consult with a healthcare
professional for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations based on
their specific symptoms and medical history. - How
long does it take to see results with homeopathic treatment for cat
scratch disease? The time it takes to see results with homeopathic
treatment for cat scratch disease may vary depending on factors such as
the individual’s overall health, the severity of symptoms, and the
specific remedy used. Some individuals may experience improvement in
symptoms within days or weeks, while others may require longer-term
treatment for optimal results.
Conclusion:
Cat scratch disease is a bacterial infection caused by
Bartonella henselae, transmitted to humans through scratches, bites, or saliva
from infected cats. While usually mild, cat scratch disease can cause
discomfort and complications, particularly in individuals with weakened immune
systems. By understanding the symptoms, identifying the causes, implementing
preventive measures, and exploring treatment options, including homeopathic
remedies, individuals can effectively manage cat scratch disease and promote
healing and recovery. With proper education, pet care practices, and holistic
healthcare approaches, individuals can enjoy a healthy, harmonious relationship
with their feline companions while minimizing the risk of cat scratch disease.