Understanding Thyroid: Symptoms, Causes, Effects and Homeopathic Medicines for Thyroid.
Introduction
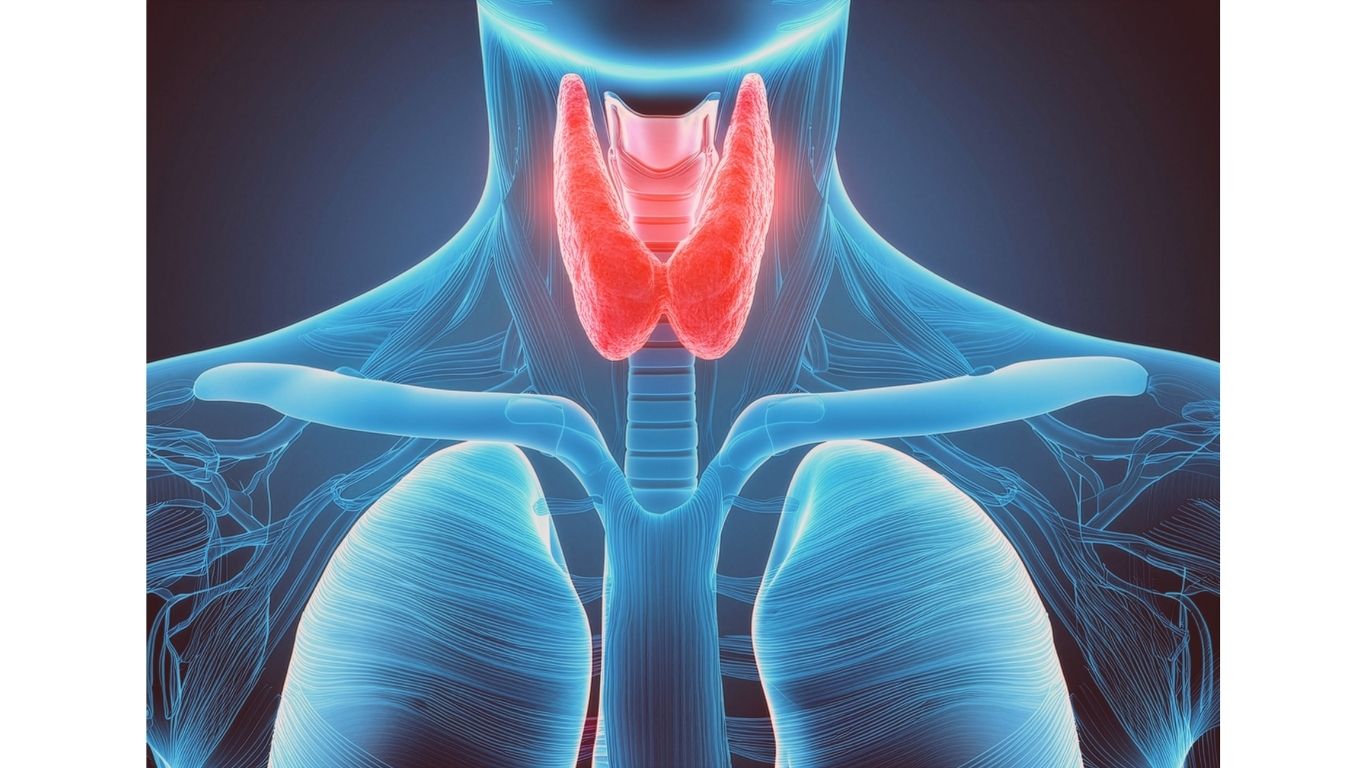
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It plays a crucial role in the body’s
metabolism and regulates various bodily functions. The thyroid gland produces hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which are essential for maintaining the body’s energy levels and regulating metabolism. These hormones influence the function of almost every organ in the body.
Thyroid Types:
There are several types of thyroid disorders, each with its own set of characteristics and implications for health. The main types include:
- Hypothyroidism:
- Description:
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). - Symptoms:
Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, hair loss, constipation, and muscle weakness are common symptoms of hypothyroidism.
- Description:
- Hyperthyroidism:
- Description:
Hyperthyroidism results from an overproduction of thyroid hormones, leading to an accelerated metabolism. - Symptoms:
Weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, insomnia, heat intolerance, and increased appetite are characteristic symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
- Description:
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis:
- Description:
An autoimmune condition, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, causing inflammation and eventual damage. - Symptoms:
Symptoms often mimic those of hypothyroidism, including fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin. Additionally, a goiter (enlarged thyroid) may be present.
- Description:
- Graves’ Disease:
- Description:
Graves’ disease is another autoimmune disorder where the immune system stimulates the thyroid to produce excessive hormones. - Symptoms:
Similar to hyperthyroidism, individuals may experience weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety. Graves’ disease is often associated with eye problems like bulging eyes (exophthalmos).
- Description:
Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders:
Thyroid disorders can manifest through a variety of symptoms, and the specific signs depend on whether the thyroid is overactive
(hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism). Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can lead to persistent fatigue, impacting daily activities and quality of life.
- Weight Changes: Hypothyroidism is associated with weight gain, while hyperthyroidism often leads to unexplained weight loss.
- Changes in Heart Rate: Hyperthyroidism may cause an increased heart rate (tachycardia), while hypothyroidism can result in a slower heart rate (bradycardia).
- Temperature Sensitivity: Individuals with hypothyroidism may feel cold all the time, while those with hyperthyroidism may experience heat intolerance.
- Mood Changes: Thyroid disorders can affect mood, leading to symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and irritability.
- Changes in Hair and Skin: Hair loss, dry skin, and brittle nails are common in hypothyroidism, while hyperthyroidism may cause sweating and thinning of hair.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Both hypo- and hyperthyroidism can lead to digestive issues, including constipation (hypothyroidism) or diarrhea (hyperthyroidism).
Causes of Thyroid Disorders:
Understanding the underlying causes of thyroid disorders is crucial for effective management. The causes can vary depending on the specific type of thyroid disorder:
- Hypothyroidism Causes:
- Autoimmune Thyroiditis: Conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis involve the immune system mistakenly attacking the thyroid gland.
- Iodine Deficiency: Insufficient iodine intake can impair the thyroid’s ability to produce hormones.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can interfere with thyroid function.
- Radiation Therapy: Previous exposure to radiation, especially to the neck and upper chest, increases the risk of hypothyroidism.
- Hyperthyroidism Causes:
- Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system stimulates the thyroid to produce excess hormones.
- Thyroid Nodules: Non-cancerous nodules on the thyroid can produce excess hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid can result in the release of stored hormones into the bloodstream.
- Excessive Iodine Intake: Consuming too much iodine, whether through diet or medication, can trigger hyperthyroidism.
Effects of Thyroid Disorders:
Thyroid disorders can have far-reaching effects on various bodily systems. Untreated or poorly managed thyroid conditions can lead to the
following complications:
- Cardiovascular Issues: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can affect the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and cholesterol imbalances.
- Mental Health Impacts: Thyroid disorders are associated with mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairments.
- Reproductive Challenges: Thyroid imbalances can interfere with reproductive health, leading to menstrual irregularities, fertility issues, and complications during pregnancy.
- Metabolic Consequences: Hypothyroidism can slow down metabolism, contributing to weight gain and fatigue, while hyperthyroidism can lead to weight loss and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Goiter: Inflammation of the thyroid (thyroiditis) or autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s or Graves’ disease can result in the enlargement of the thyroid gland, known as a goiter.
Prevention and management of thyroid disorders involve a few
key strategies:
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet that includes iodine-rich foods like seafood, dairy products, and iodized salt is essential for proper thyroid function. Additionally, including foods rich in selenium (Brazil nuts, legumes, fish, and eggs) and zinc (oysters, lean meats, poultry, and whole grains) can support thyroid health.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can affect the thyroid gland. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or exercise can be beneficial.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps to boost metabolism and maintain a healthy weight, which can support thyroid function.
- Avoiding Environmental Toxins: Exposure to certain environmental toxins like radiation, heavy metals, and industrial chemicals can impact thyroid function. Minimizing exposure to these substances is crucial.
Effective Homeopathic Medicines for Thyroid Disorders:
Homeopathy, a holistic system of medicine, offers individualized and natural approaches to managing thyroid disorders. It focuses
on treating the root cause of the condition, aiming to restore balance to the body. While homeopathic remedies should be considered complementary to conventional medical treatment, they may offer relief from symptoms and support overall well-being. Some common homeopathic remedies for thyroid disorders include:
- Iodum (Iodine): Used for both hypo- and hyperthyroidism, Iodum is indicated when there is a sense of internal heat, restlessness, and anxiety.
- Thyroidinum: This remedy is derived from the thyroid gland itself and is often prescribed for various thyroid disorders, helping to regulate hormone production.
- Lycopodium: Suitable for individuals with hypothyroidism, Lycopodium is indicated when there is weight gain, digestive issues, and a preference for warm drinks.
- Natrum Muriaticum: Useful for hypothyroidism, Natrum Muriaticum is recommended when there is a tendency to gain weight, salt cravings, and emotional suppression.
- Calcarea Carbonica: Indicated for hypothyroidism with symptoms such as fatigue, sensitivity to cold, and weight gain, especially around the abdomen.
It’s important to note that homeopathic remedies should be chosen based on an individual’s specific symptoms and constitution.
Consultation with a qualified homeopathic practitioner is advised for personalized treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is homeopathy, and how does it approach thyroid disorders? Homeopathy is a holistic system of medicine that aims to
stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms. In treating thyroid disorders, homeopathic medicine focuses on addressing underlying imbalances, promoting overall well-being, and supporting the thyroid gland’s optimal function.
2. Can homeopathic medicine cure thyroid disorders completely? Homeopathic medicine aims to alleviate symptoms, improve
thyroid function, and enhance overall health. While it may provide relief and support, claiming a complete cure can vary among individuals. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is essential for a comprehensive approach to thyroid health.
3. Which homeopathic remedies are commonly used for thyroid conditions? Popular homeopathic remedies for thyroid disorders
include Thyroidinum, Iodum, Lycopodium clavatum, and Calcarea carbonica. The selection of a specific remedy depends on the individual’s symptoms, overall health, and the unique characteristics of their thyroid condition.
4. Is it safe to combine homeopathic medicine with conventional thyroid medications? It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare
professional before combining homeopathic medicine with conventional thyroid medications. They can assess potential interactions and help create a treatment plan that ensures the safety and effectiveness of both approaches.
5. How long does it take to see results with homeopathic medicine for thyroid disorders? The time to observe results with
homeopathic medicine varies among individuals and depends on factors such as the severity of the thyroid disorder, overall health, and adherence to the treatment plan. Regular follow-up with a qualified practitioner is recommended for monitoring progress.
6. Can homeopathic medicine be used as a sole treatment for thyroid disorders? While homeopathic medicine may offer support for
thyroid disorders, it is not advisable to use it as the sole treatment. A comprehensive approach that includes regular medical monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, and collaboration with healthcare professionals is essential for managing thyroid conditions effectively.
7. Are there lifestyle changes that complement homeopathic medicine for thyroid health? Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for managing thyroid disorders. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep. Combining these lifestyle changes with homeopathic medicine can contribute to overall well-being and thyroid health.
8. Can homeopathic medicine prevent thyroid disorders? Homeopathic medicine focuses on restoring balance and supporting the body’s self-healing abilities, but it cannot guarantee the prevention of thyroid disorders. A proactive approach to a healthy lifestyle, regular check-ups, and appropriate preventive measures recommended by healthcare professionals are essential for thyroid health.
9. Is it advisable to self-prescribe homeopathic medicine for thyroid disorders? Self-prescribing homeopathic medicine for thyroid
disorders is not recommended. A qualified homeopathic practitioner can assess your specific symptoms, overall health, and the unique aspects of your thyroid condition to prescribe the most appropriate remedies.
10. Where can I find a qualified homeopathic practitioner for thyroid concerns? Qualified homeopathic practitioners can be found
through reputable healthcare directories, recommendations from healthcare professionals, or by contacting recognized homeopathic associations. Always ensure that the practitioner has the necessary credentials and experience in treating thyroid conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, thyroid disorders are complex conditions that can have a profound impact on physical and mental health. Recognizing the
symptoms, understanding the causes, and exploring various treatment options, including homeopathic remedies, are essential components of comprehensive thyroid care.
A holistic approach to thyroid health involves collaboration between conventional medicine and complementary therapies, such as homeopathy. Individuals experiencing symptoms of thyroid disorders should seek professional medical advice for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can contribute to overall thyroid well-being.
Public awareness and education are crucial in dispelling myths and misconceptions about thyroid disorders. By fostering a better
understanding of thyroid health, we can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards prevention, early detection, and effective management of thyroid disorders. Remember, a holistic and informed approach is key to maintaining optimal thyroid function and overall well-being.
Thanks for feedback. You can see my post on AOL read more.