Discover Symptoms, Causes and Effective Homeopathic Remedies for Arteriosclerosis. Learn how to prevent this condition today.
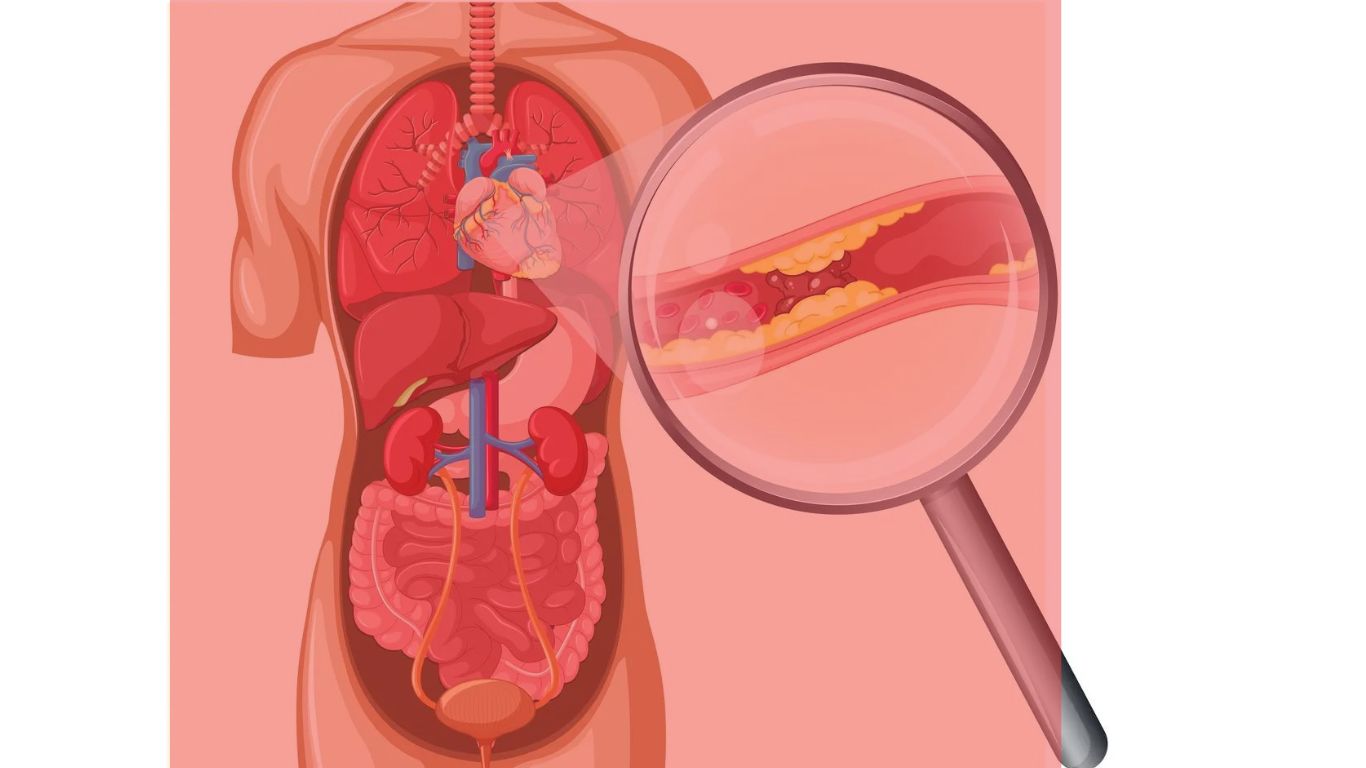
Arteriosclerosis is a chronic condition characterized by the thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the arterial walls. It is a common condition that tends to develop with age and is a major contributing factor to cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. The term “arteriosclerosis” is often used interchangeably with “atherosclerosis,” although atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis involving the buildup of fatty deposits, or plaques, inside the arteries. Understanding arteriosclerosis is crucial for early detection, effective management, and prevention of its complications, including the role that homeopathic remedies can play in supporting cardiovascular health.
Understanding Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis is a broad term encompassing various conditions that lead to the stiffening and narrowing of arteries. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Healthy arteries are flexible, strong, and elastic, allowing them to efficiently transport blood. However, with arteriosclerosis, the arteries become thickened and rigid, which can impede blood flow and lead to serious health problems.
Types of Arteriosclerosis
There are three main types of arteriosclerosis:
- Atherosclerosis: The most common form of arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, occurs when the inner lining of the arteries (the endothelium) becomes damaged and cholesterol, fats, and other substances accumulate to form plaques. These plaques can harden over time, causing the arteries to narrow and restrict blood flow. Atherosclerosis can affect any artery in the body but is most commonly found in the coronary arteries (supplying the heart), carotid arteries (supplying the brain), and peripheral arteries (supplying the limbs).
- Arteriolosclerosis: This type involves the thickening of the walls of the small arteries and arterioles, which are the smaller branches of arteries. Arteriolosclerosis is commonly associated with high blood pressure (hypertension) and diabetes. It primarily affects the kidneys and other vital organs.
- Mönckeberg’s Arteriosclerosis: Also known as medial calcific sclerosis, this type is characterized by the calcification of the tunica media, the middle layer of the artery wall. Unlike atherosclerosis, Mönckeberg’s arteriosclerosis does not necessarily involve the buildup of plaques and typically affects the medium-sized arteries. It is more common in the elderly and those with diabetes.
Symptoms of Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis often develops gradually over many years, and in its early stages, it may not cause any symptoms. Symptoms typically arise when the affected arteries become significantly narrowed or blocked, leading to reduced blood flow to various organs and tissues.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of arteriosclerosis depend on the location and severity of the affected arteries:
- Coronary Arteries (Heart): When arteriosclerosis affects the coronary arteries, it can lead to coronary artery disease (CAD), resulting in symptoms such as:
- Angina Pectoris: Chest pain or discomfort, often triggered by physical activity or stress.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during exertion.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness, particularly during or after physical activity.
- Heart Attack: A sudden blockage of a coronary artery can lead to a heart attack, characterized by severe chest pain, sweating, nausea, and shortness of breath.
- Carotid Arteries (Brain): Arteriosclerosis in the carotid arteries can lead to reduced blood flow to the brain, resulting in:
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): Also known as a “mini stroke,” TIA is a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain, causing symptoms such as sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, slurred speech, confusion, and dizziness.
- Stroke: A complete blockage of a carotid artery can lead to a stroke, with more severe and lasting symptoms similar to those of TIA.
- Peripheral Arteries (Limbs): When arteriosclerosis affects the arteries that supply blood to the limbs, it can lead to peripheral artery disease (PAD), with symptoms including:
- Intermittent Claudication: Pain, cramping, or weakness in the legs or arms, especially during physical activity.
- Coldness or Numbness: Affected limbs may feel cold or numb due to reduced blood flow.
- Non-healing Wounds: Sores or ulcers on the feet or legs that heal slowly or not at all.
- Renal Arteries (Kidneys): Arteriosclerosis in the renal arteries can lead to reduced blood flow to the kidneys, resulting in:
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension that is difficult to control with medication.
- Kidney Dysfunction: Symptoms of kidney disease, such as fatigue, swelling, and changes in urination.
Causes of Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis is a complex condition with multiple contributing factors. The development of arteriosclerosis is typically a result of a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
- Aging: The risk of arteriosclerosis increases with age. As we age, the arteries naturally become less flexible and more prone to thickening and hardening.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Chronic high blood pressure damages the artery walls, making them more susceptible to thickening and the formation of plaques.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol contribute to the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage the blood vessels, increasing the risk of arteriosclerosis.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the endothelium (the inner lining of the arteries), promotes the buildup of plaques, and contributes to the hardening of the arteries.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, all of which are risk factors for arteriosclerosis.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to obesity, high blood pressure, and poor cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of arteriosclerosis.
- Unhealthy Diet: A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium promotes the development of atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis.
- Genetics: A family history of cardiovascular disease increases the risk of arteriosclerosis.
- Chronic Inflammation: Inflammation in the body, whether due to infection, autoimmune disease, or other factors, can contribute to the development of arteriosclerosis by promoting the buildup of plaques in the arteries.
Effects of Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis can have a wide range of effects on the body, depending on which arteries are affected and the severity of the condition. The consequences of arteriosclerosis can be serious and life-threatening, particularly if it leads to the obstruction of blood flow to vital organs.
Immediate Effects
- Reduced Blood Flow: The primary effect of arteriosclerosis is the narrowing and hardening of arteries, which reduces blood flow to the organs and tissues that depend on those arteries. This can lead to ischemia (a lack of oxygen and nutrients) in the affected areas.
- Chest Pain (Angina): When the coronary arteries are affected, reduced blood flow to the heart muscle can cause chest pain or discomfort, known as angina.
- Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs): Reduced blood flow to the brain due to arteriosclerosis in the carotid arteries can cause TIAs, which are warning signs of a potential stroke.
- Intermittent Claudication: Reduced blood flow to the limbs due to arteriosclerosis in the peripheral arteries can cause pain and cramping during physical activity, known as intermittent claudication.
Long-term Effects
- Heart Attack: If a plaque in a coronary artery rupture, it can trigger the formation of a blood clot that completely blocks blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to a heart attack (myocardial infarction).
- Stroke: A complete blockage of a carotid artery due to arteriosclerosis can lead to a stroke, resulting in permanent brain damage or death.
- Heart Failure: Chronic ischemia (reduced blood flow) due to arteriosclerosis can weaken the heart muscle over time, leading to heart failure, a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Severe PAD can lead to chronic pain, non-healing wounds, and in some cases, gangrene (tissue death), which may require amputation.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Reduced blood flow to the kidneys due to arteriosclerosis in the renal arteries can lead to chronic kidney disease, which can progress to kidney failure.
- Aneurysm: Arteriosclerosis can weaken the walls of an artery, leading to the formation of an aneurysm (a bulging or ballooning of the artery). If an aneurysm ruptures, it can cause life-threatening internal bleeding.
Prevention of Arteriosclerosis
Preventing arteriosclerosis involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors that contribute to the development of the condition. Here are some key strategies for preventing arteriosclerosis:
Lifestyle Changes
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for arteriosclerosis. Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of developing the condition and improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats (such as those found in fish, nuts, and olive oil) can help reduce cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and the risk of arteriosclerosis. Limiting the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol is also important.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, lowers blood pressure, improves cholesterol levels, and reduces the risk of diabetes. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, and other conditions that contribute to arteriosclerosis.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Drinking alcohol in moderation, if at all, can help reduce the risk of high blood pressure and obesity, both of which contribute to arteriosclerosis.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can increase the risk of arteriosclerosis by raising blood pressure and promoting unhealthy behaviors such as overeating and smoking. Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and relaxation exercises can help reduce stress levels.
Medical Management
- Control Blood Pressure: Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure are essential for preventing arteriosclerosis. Medication may be necessary for individuals with hypertension.
- Manage Cholesterol Levels: Keeping cholesterol levels within a healthy range is crucial for preventing the buildup of plaques in the arteries. Statins and other cholesterol-lowering medications may be prescribed.
- Manage Diabetes: If you have diabetes, controlling your blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication is crucial for reducing the risk of arteriosclerosis.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups and monitoring of cardiovascular health can help detect early signs of arteriosclerosis and allow for timely intervention.
Homeopathic Treatment for Arteriosclerosis
Homeopathy is a system of alternative medicine that uses highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes. Homeopathic remedies for arteriosclerosis aim to improve blood circulation, reduce the risk of complications, and support overall cardiovascular health.
Key Homeopathic Remedies for Arteriosclerosis
- Aurum Metallicum: Aurum is often indicated for individuals with atherosclerosis, particularly when there is a history of high blood pressure, depression, and a tendency to anger or irritability. It is used to improve blood flow, reduce cholesterol levels, and support heart health.
- Baryta Carbonica: This remedy is useful for elderly individuals with arteriosclerosis, particularly when there is mental or physical weakness, memory loss, and a tendency to develop aneurysms. Baryta Carbonica helps improve circulation and strengthen the arterial walls.
- Crataegus Oxyacantha: Crataegus, also known as hawthorn, is a well-known heart tonic in homeopathy. It is used to improve heart function, strengthen the heart muscle, and relieve symptoms of arteriosclerosis, such as angina and palpitations.
- Plumbum Metallicum: Plumbum is indicated for individuals with arteriosclerosis who experience symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, and pain in the limbs. It is used to improve circulation and reduce the risk of complications such as peripheral artery disease.
- Secale Cornutum: This remedy is useful for individuals with arteriosclerosis who experience symptoms such as coldness, numbness, and tingling in the extremities. Secale Cornutum helps improve blood flow and prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Calcarea Fluorica: Calcarea Fluorica is indicated for individuals with hardened arteries and a tendency to develop varicose veins or aneurysms. It helps improve the elasticity of the arterial walls and support overall cardiovascular health.
- Nux Vomica: Nux Vomica is recommended for individuals with arteriosclerosis who have a history of high blood pressure, digestive issues, and a tendency to stress and irritability. It is used to improve circulation, support liver function, and reduce the risk of complications.
- Tabacum: This remedy is indicated for individuals with arteriosclerosis who have a history of smoking and experience symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, and coldness in the limbs. Tabacum helps improve circulation and support heart health.
Individualized Homeopathic Treatment
Homeopathy is a highly individualized form of treatment, and the choice of remedy depends on the specific symptoms, personality, and constitution of the individual. A trained homeopathic practitioner will take a detailed case history, including physical, emotional, and mental symptoms, to select the most appropriate remedy.
It is important to note that homeopathic remedies should be used under the guidance of a qualified homeopathic practitioner, especially in the case of a serious condition like arteriosclerosis. Homeopathy can be used alongside conventional medical treatment, but it should not replace it in cases of acute or life-threatening conditions.
FAQs About Homeopathic Medicines for Arteriosclerosis
1. What is arteriosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis is a condition characterized by the thickening and hardening of the arterial walls, which can lead to reduced blood flow and increased risk of cardiovascular problems. This condition often results from the buildup of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis) or changes in the arterial structure due to aging or other factors.
2. How can homeopathic medicines help with arteriosclerosis?
Homeopathic medicines aim to support cardiovascular health by addressing underlying imbalances and improving circulation. They may help alleviate symptoms associated with arteriosclerosis, such as chest pain, reduced blood flow, and high blood pressure. Homeopathic remedies work by stimulating the body’s natural healing processes and supporting overall arterial health.
3. Which homeopathic remedies are commonly used for arteriosclerosis?
Several homeopathic remedies may be considered for managing arteriosclerosis, including:
- Aurum Metallicum: Often used for individuals with hardened arteries and associated symptoms like high blood pressure and emotional distress.
- Crataegus Oxyacantha: Known for its benefits to heart health, it helps strengthen the heart muscle and improve circulation.
- Calcarea Fluorica: Helps with arterial hardening and improves the elasticity of the arterial walls.
- Natrum Muriaticum: Useful for individuals with arteriosclerosis who experience symptoms such as weakness and emotional stress.
4. How should homeopathic remedies be selected for arteriosclerosis?
The selection of homeopathic remedies for arteriosclerosis depends on individual symptoms, overall health, and specific characteristics of the condition. A qualified homeopathic practitioner will conduct a thorough assessment to determine the most appropriate remedy based on the patient’s unique symptoms and constitution.
5. Are homeopathic remedies safe for arteriosclerosis?
Homeopathic remedies are generally considered safe due to their highly diluted nature. However, they should be used under the guidance of a qualified homeopathic practitioner, especially when managing a serious condition like arteriosclerosis. It is important to continue conventional treatments and consult with a healthcare provider for a comprehensive approach to managing arteriosclerosis.
6. Can homeopathic remedies replace conventional treatments for arteriosclerosis?
Homeopathic remedies are intended to complement, not replace, conventional medical treatments. While they may help alleviate symptoms and support overall cardiovascular health, conventional treatments such as medications, lifestyle changes, and medical procedures are crucial for managing arteriosclerosis and preventing complications.
7. How long does it take to see results from homeopathic remedies for arteriosclerosis?
The time required to see results from homeopathic remedies can vary depending on the individual, the severity of the condition, and the specific remedy used. Some individuals may notice improvements in symptoms within a few weeks, while others may take longer. Regular follow-up with a homeopathic practitioner can help monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
8. Are there any side effects associated with homeopathic remedies for arteriosclerosis?
Homeopathic remedies are typically associated with minimal side effects due to their extreme dilution. However, individual responses can vary. It is important to work with a qualified practitioner to ensure the remedies are suitable and to address any concerns or adverse effects that may occur.
9. Can lifestyle changes enhance the effectiveness of homeopathic remedies for arteriosclerosis?
Yes, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can enhance the effectiveness of homeopathic remedies. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These changes support overall cardiovascular health and improve the effectiveness of complementary treatments.
10. Where can I find a qualified homeopathic practitioner for arteriosclerosis?
To find a qualified homeopathic practitioner, you can seek recommendations from your healthcare provider, search online directories of professional homeopathic organizations, or contact local homeopathy clinics. It is important to choose a practitioner with appropriate credentials and experience in treating cardiovascular conditions like arteriosclerosis.
Conclusion
Arteriosclerosis is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires careful management and prevention. Understanding the symptoms, causes, effects, and prevention strategies is essential for reducing the risk of complications and improving quality of life. While conventional medical treatments are crucial for managing arteriosclerosis, homeopathy offers a complementary approach that can help relieve symptoms, support cardiovascular health, and address the underlying causes of the condition.
By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals with arteriosclerosis can lead a fulfilling life and reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other complications. Homeopathy, when used appropriately, can be a valuable part of a comprehensive treatment plan for arteriosclerosis, providing gentle, natural support for heart health and overall well-being.