Homeopathic Remedies for Sterility: Effective Homeo Remedies. If you are seeking effective homeopathic remedies for sterility, look no further. Our comprehensive guide on homeopathic medicines for sterility provides valuable insights and solutions. With our expert-recommended treatments, you can explore natural and effective options to address sterility concerns.
Introduction
Sterility, commonly referred to as infertility, is a condition that affects countless individuals and couples worldwide. Despite advances in medical science, sterility remains a challenging issue, often leading to emotional distress, societal stigma, and personal frustration. Understanding sterility is crucial not only for those directly affected but also for society as a whole, as it influences population dynamics, family structures, and even socio-economic trends.
Sterility is typically defined as the inability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse. It can affect both men and women, and the causes are often multifaceted, involving physiological, psychological, and environmental factors. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms, causes, effects, prevention strategies, and homeopathic treatments for sterility.
Symptoms of Sterility
Sterility is often a silent condition, with many individuals unaware of their reproductive challenges until they attempt to conceive. However, there are some symptoms and signs that may indicate potential sterility issues.
1. Irregular Menstrual Cycles
For women, one of the most common indicators of potential sterility is irregular menstrual cycles. This includes cycles that are unusually short or long, heavy or light periods, or significant changes in the menstrual pattern. These irregularities can signal underlying hormonal imbalances or reproductive organ dysfunctions, which can contribute to infertility.
2. Painful Menstruation
Severe menstrual pain (dysmenorrhea) can be a sign of conditions like endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), both of which can lead to sterility. Women experiencing chronic pelvic pain, especially during menstruation, should seek medical evaluation as it might indicate underlying reproductive health issues.
3. Absence of Menstruation (Amenorrhea)
The absence of menstruation, known as amenorrhea, is a significant red flag. Primary amenorrhea (when a woman has never menstruated) or secondary amenorrhea (when menstruation ceases after it has previously occurred) can be caused by various factors, including hormonal imbalances, extreme weight loss, or stress, all of which can affect fertility.
4. Hormonal Fluctuations
Hormonal imbalances are often indicated by symptoms such as unexplained weight gain, severe acne, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), or hair loss. These symptoms might suggest conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is a leading cause of female infertility.
5. Pain During Intercourse
Dyspareunia, or painful intercourse, can be a symptom of underlying conditions such as infections, endometriosis, or pelvic inflammatory disease, all of which can impact fertility.
6. Recurrent Miscarriages
While miscarriages are not uncommon, recurrent miscarriages (two or more consecutive losses) might indicate underlying reproductive issues that could lead to sterility. Factors contributing to recurrent miscarriages include uterine abnormalities, hormonal disorders, or genetic issues.
7. Male Symptoms
Men may also exhibit symptoms that suggest sterility, such as changes in sexual function, reduced sexual desire, pain or swelling in the testicles, difficulty maintaining an erection, or issues with ejaculation. Additionally, men may experience reduced facial or body hair, which could indicate a hormonal issue related to fertility.
Causes of Sterility
Sterility can be caused by a wide range of factors, which can affect either the male or female partner, or both. Understanding these causes is essential for diagnosis and treatment.
1. Ovulation Disorders
Ovulation disorders are among the most common causes of female infertility. These disorders can be caused by hormonal imbalances, which can result from conditions like PCOS, hyperprolactinemia (excess prolactin), or thyroid dysfunctions. When ovulation does not occur regularly, or at all, the chances of conception are significantly reduced.
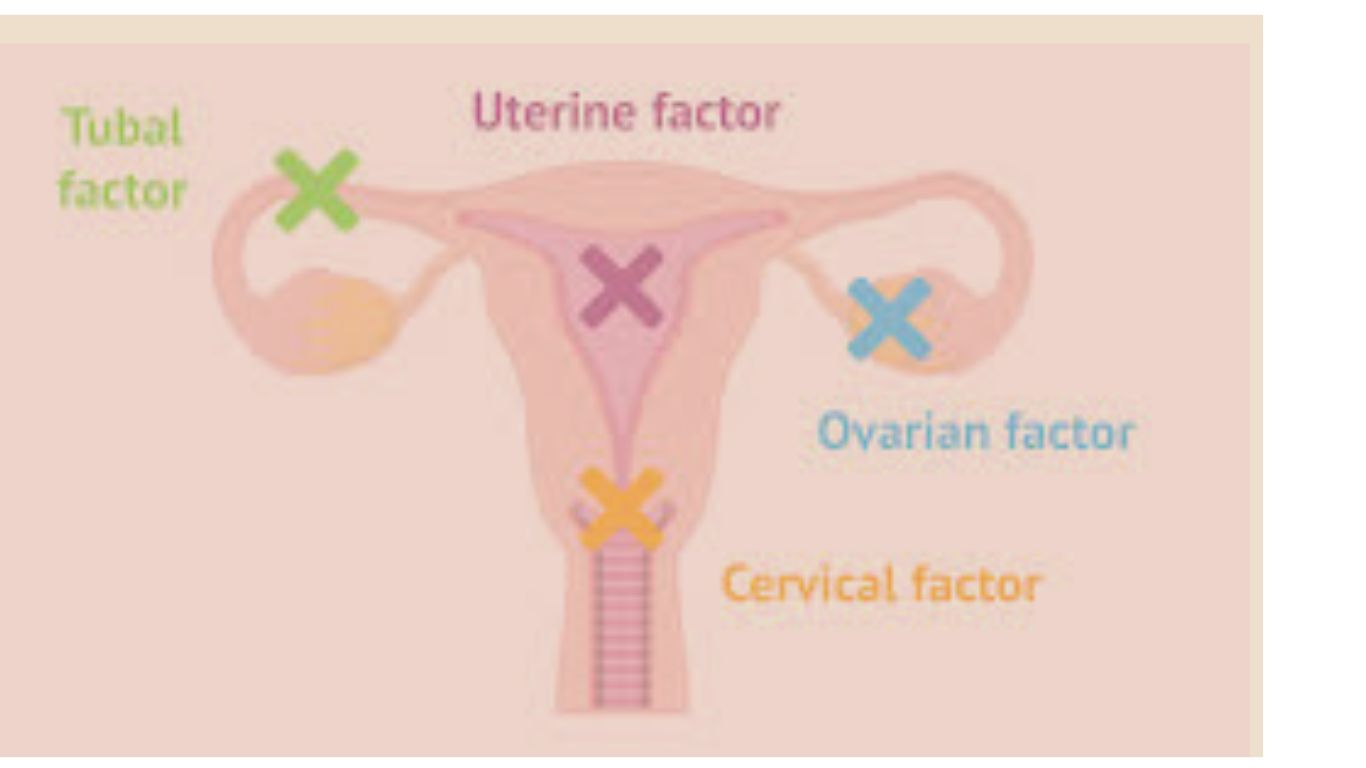
2. Tubal Infertility
The fallopian tubes play a critical role in conception by allowing the sperm to meet the egg. Blockages or damage to the fallopian tubes, often due to infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease, previous surgeries, or conditions like endometriosis, can prevent this from happening, leading to sterility.
3. Uterine or Cervical Abnormalities
Structural issues with the uterus or cervix can also lead to infertility. Uterine fibroids, polyps, or congenital uterine abnormalities can interfere with implantation or increase the risk of miscarriage. Cervical stenosis (narrowing of the cervix) or abnormal cervical mucus can also hinder sperm from reaching the egg.
4. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus grows outside it, often on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic structures. This can cause severe pain and is a leading cause of infertility, as it can interfere with the function of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus.
5. Male Factor Infertility
Male infertility is responsible for approximately 30-40% of infertility cases. Causes include low sperm count, poor sperm motility, abnormal sperm morphology, and issues with sperm delivery (e.g., erectile dysfunction or ejaculation problems). Hormonal imbalances, genetic disorders, or environmental factors such as exposure to toxins can also affect male fertility.
6. Age
Age is a significant factor in fertility, particularly for women. As women age, the quantity and quality of their eggs decline, making conception more difficult. After age 35, a woman’s fertility begins to decrease more rapidly, and by age 40, the chances of natural conception are significantly lower. Men’s fertility also declines with age, but typically at a slower rate.
7. Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices can have a profound impact on fertility. Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, poor diet, obesity, and lack of exercise can all contribute to infertility. Chronic stress and exposure to environmental toxins (such as pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial chemicals) can also negatively affect reproductive health.
8. Medical Conditions and Treatments
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and thyroid diseases, can impact fertility. Additionally, treatments for cancer, such as chemotherapy or radiation, can damage reproductive organs and lead to sterility. Surgical procedures involving the reproductive organs may also result in scarring or damage that impairs fertility.
9. Genetic Factors
Genetic abnormalities can play a role in infertility. Chromosomal abnormalities, such as Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, or translocations, can affect reproductive function. Genetic mutations that affect sperm or egg production can also lead to sterility.
10. Unexplained Infertility
In some cases, couples may experience infertility with no identifiable cause. This is known as unexplained infertility, and it can be particularly frustrating for those affected. Despite extensive testing, no clear reason for the infertility can be found, making treatment more challenging.
Effects of Sterility
The effects of sterility can be profound, impacting individuals, couples, and society in various ways.
1. Emotional and Psychological Impact
The inability to conceive can lead to a range of emotional and psychological effects. Individuals and couples may experience feelings of inadequacy, guilt, anger, and depression. The stress of infertility can strain relationships, leading to communication breakdowns and marital discord. The societal pressure to have children can exacerbate these feelings, leading to isolation and anxiety.
2. Social and Cultural Impact
In many cultures, fertility is highly valued, and the inability to conceive can lead to stigma and discrimination. Women, in particular, may face social ostracism, as they are often unfairly blamed for infertility. This can result in strained family relationships, loss of social status, and even divorce in some cases.
3. Economic Impact
The financial burden of infertility treatments can be significant. Many fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), are expensive and may not be covered by insurance. The costs of repeated treatments, along with the emotional toll, can lead to financial stress and debt.
4. Impact on Quality of Life
Infertility can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. The constant focus on conceiving, the emotional rollercoaster of hope and disappointment, and the physical demands of treatments can take a toll on overall well-being. The inability to achieve a desired family size can lead to long-term dissatisfaction and regret.
5. Impact on Relationships
The strain of infertility can affect relationships not only between partners but also with family and friends. The pressure to conceive, coupled with the emotional and financial stress, can lead to conflicts and misunderstandings. Couples may struggle with intimacy issues, and the emotional burden may lead to withdrawal from social activities and support networks.
Prevention of Sterility
While not all causes of sterility can be prevented, certain steps can be taken to reduce the risk of infertility. Prevention strategies focus on maintaining reproductive health, addressing lifestyle factors, and seeking timely medical intervention.
1. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for fertility. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can positively impact reproductive health. Avoiding smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use is also important, as these substances can damage reproductive organs and impair fertility.
2. Managing Stress
Chronic stress can negatively affect fertility by disrupting hormonal balance and menstrual cycles. Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and counseling can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
3. Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups can help detect potential fertility issues early. Women should monitor their menstrual cycles and seek medical advice if they notice any irregularities. Men should also be proactive in addressing any concerns related to sexual function or reproductive health.
4. Protecting Reproductive Health
Practicing safe sex and avoiding sexually transmitted infections (STIs) is crucial for protecting reproductive health. Untreated STIs can lead to complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease, which can cause infertility. Vaccinations, such as the HPV vaccine, can also help prevent infections that may impact fertility.
5. Avoiding Environmental Toxins
Exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial chemicals, can harm reproductive health. Individuals should take precautions to minimize exposure by using protective gear, avoiding contaminated areas, and choosing organic foods when possible.
6. Seeking Early Medical Intervention
If a couple has been trying to conceive for a year without success, they should seek medical evaluation. Early intervention can help identify and address potential fertility issues before they become more severe. Timely treatment of conditions such as endometriosis, PCOS, or infections can improve the chances of conception.
7. Understanding Age-Related Risks
Both men and women should be aware of the impact of age on fertility. Women, in particular, should understand that fertility declines with age, especially after 35. Couples should consider family planning early and seek advice from a healthcare provider if they plan to delay childbearing.
8. Avoiding Overuse of Fertility Treatments
While fertility treatments can be effective, they should be used judiciously. Overuse or improper use of treatments can lead to complications, including multiple pregnancies, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, or long-term health issues. Couples should work closely with a fertility specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Homeopathic Treatments for Sterility
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to treating sterility by addressing the underlying causes and restoring balance to the body. Homeopathic remedies are chosen based on the individual’s physical, emotional, and psychological state, making the treatment highly personalized. Below are some commonly used homeopathic remedies for sterility.
1. Sepia
Sepia is often prescribed for women experiencing infertility due to hormonal imbalances or conditions such as PCOS. It is particularly useful for women who experience irregular or absent periods, painful menstruation, or a sensation of bearing down in the pelvic region. Sepia is also beneficial for women who feel emotionally drained or disconnected.
2. Pulsatilla
Pulsatilla is indicated for women with irregular menstrual cycles, particularly when the flow is changeable and associated with emotional sensitivity. It is also helpful for women who experience scanty or delayed periods and for those who feel better in fresh air and prefer open spaces. Pulsatilla can help restore hormonal balance and improve fertility.
3. Calcarea Carbonica
Calcarea Carbonica is often used for women who have a tendency to gain weight, feel cold, and experience profuse sweating, particularly on the head. It is beneficial for women with irregular or heavy periods, and those who are prone to anxiety and fatigue. Calcarea Carbonica can help regulate menstrual cycles and support reproductive health.
4. Natrum Muriaticum
Natrum Muriaticum is indicated for women who experience irregular or absent periods, particularly when associated with emotional stress or grief. It is also beneficial for women who feel emotionally reserved or introverted. Natrum Muriaticum can help restore emotional balance and improve fertility.
5. Agnus Castus
Agnus Castus is a valuable remedy for both men and women experiencing infertility. In women, it is used for conditions such as amenorrhea or scanty periods, often associated with low libido. In men, it is beneficial for those with low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or sexual dysfunction. Agnus Castus can help regulate hormonal levels and improve reproductive health.
6. Silicea
Silicea is often prescribed for individuals who are prone to infections, particularly of the reproductive organs. It is beneficial for women with a history of chronic pelvic inflammatory disease or recurrent infections. Silicea can help strengthen the immune system and support reproductive health.
7. Lycopodium
Lycopodium is indicated for individuals with digestive issues, liver disorders, or a tendency to develop varicose veins. In women, it is beneficial for those with irregular periods, ovarian cysts, or a sensation of fullness in the abdomen. In men, it is used for low sperm count or erectile dysfunction. Lycopodium can help improve overall vitality and reproductive health.
8. Sabina
Sabina is often used for women who experience recurrent miscarriages or heavy, painful menstruation. It is particularly beneficial for women who feel a strong bearing down sensation in the pelvic region. Sabina can help prevent miscarriages and support a healthy pregnancy.
9. Sulphur
Sulphur is indicated for individuals with a tendency towards skin issues, heat sensitivity, and a strong desire for spicy foods. It is beneficial for women with irregular periods, particularly when associated with hot flashes or burning sensations. Sulphur can help regulate hormonal balance and improve fertility.
10. Homeopathic Consultation
It is essential to consult with a qualified homeopathic practitioner to determine the most appropriate remedy for sterility. Homeopathy treats the individual as a whole, considering physical, emotional, and psychological factors. A detailed case history and consultation are necessary to select the correct remedy and dosage.
FAQs About Homeopathic Medicines for Sterility
1. What is sterility in the context of homeopathic medicine?
Sterility, in homeopathic medicine, refers to a condition where an individual is unable to conceive or produce offspring. It can affect both men and women and may be attributed to various physical or emotional factors. Homeopathy aims to address the underlying causes of sterility by considering the individual’s overall health and constitutional factors.
2. How does homeopathy approach the treatment of sterility?
Homeopathy approaches the treatment of sterility by providing personalized remedies based on the individual’s specific symptoms, health history, and emotional state. Homeopathic remedies are selected to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes and restore balance. The treatment is holistic, considering both physical and psychological aspects of the condition.
3. What are some common homeopathic remedies used for sterility?
Common homeopathic remedies for sterility include:
- Sepia: Often used for women with hormonal imbalances and emotional detachment.
- Lycopodium: Helpful for men and women with low self-esteem and digestive issues.
- Natrum Muriaticum: Used for those with past emotional trauma affecting fertility.
- Sulphur: Beneficial for individuals with general weakness and a tendency towards chronic infections.
The choice of remedy depends on the individual’s specific symptoms and health profile.
4. Can homeopathic remedies improve fertility in both men and women?
Yes, homeopathic remedies can support fertility in both men and women by addressing underlying causes and imbalances that may be contributing to sterility. For women, remedies may focus on hormonal balance and reproductive health, while for men, remedies may target issues like low sperm count or vitality.
5. How long does it typically take to see results from homeopathic treatment for sterility?
The time required to see results from homeopathic treatment for sterility can vary depending on several factors, including the underlying cause of sterility, the individual’s overall health, and adherence to the treatment plan. Some individuals may experience improvements within a few months, while others may take longer. Consistent follow-up with a homeopathic practitioner is essential for monitoring progress and making necessary adjustments.
6. Are homeopathic remedies safe to use alongside conventional treatments for sterility?
Homeopathic remedies are generally considered safe and can be used alongside conventional treatments. However, it is crucial to consult with both a homeopathic practitioner and a conventional healthcare provider to ensure that there are no potential interactions or contraindications. Combining therapies should be done under professional guidance to achieve the best outcomes.
7. Can lifestyle changes complement homeopathic treatment for sterility?
Yes, lifestyle changes can complement homeopathic treatment for sterility. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding harmful substances, can support overall reproductive health and enhance the effectiveness of homeopathic remedies.
8. How do I choose the right homeopathic remedy for sterility?
Choosing the right homeopathic remedy for sterility involves a thorough consultation with a qualified homeopathic practitioner. The practitioner will evaluate your specific symptoms, medical history, and emotional state to select the most appropriate remedy. Personalized treatment is crucial for addressing the unique aspects of your condition.
9. Are there any known side effects of homeopathic remedies for sterility?
Homeopathic remedies are generally well-tolerated and considered safe when used as directed. Since homeopathic remedies are highly diluted, the risk of side effects is minimal. However, individuals should consult with a homeopathic practitioner to ensure that the chosen remedy is suitable for their specific condition and health profile.
10. How can I find a qualified homeopathic practitioner for sterility?
To find a qualified homeopathic practitioner, consider seeking recommendations from healthcare providers, friends, or family members. Additionally, you can search for practitioners through professional homeopathic associations or organizations. Ensure that the practitioner is licensed and experienced in treating fertility and sterility issues.
Conclusion
Sterility is a complex condition with far-reaching effects on individuals, couples, and society. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and effects of sterility is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. While conventional medicine offers various treatments for infertility, homeopathy provides a holistic approach that addresses the underlying causes and promotes overall well-being.
Preventive measures, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking early medical intervention, can reduce the risk of infertility. For those already experiencing sterility, homeopathy offers a personalized and gentle approach to treatment, with remedies selected based on the individual’s unique constitution.
By addressing sterility with compassion and understanding, we can help individuals and couples navigate this challenging journey and improve their chances of achieving their dream of parenthood.