Explore Gangrene: Symptoms, causes, effects, prevention and Homeopathic Medicines for Gangrene
Introduction
Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a loss of blood flow, infection, or trauma causes the death of body tissue. It can affect any part of the body but is most commonly seen in the extremities, such as the toes, fingers, feet, and hands. In severe cases, it can also impact internal organs. Understanding gangrene, its symptoms, causes, effects, prevention methods, and treatment options, including homeopathic remedies, is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Symptoms of Gangrene
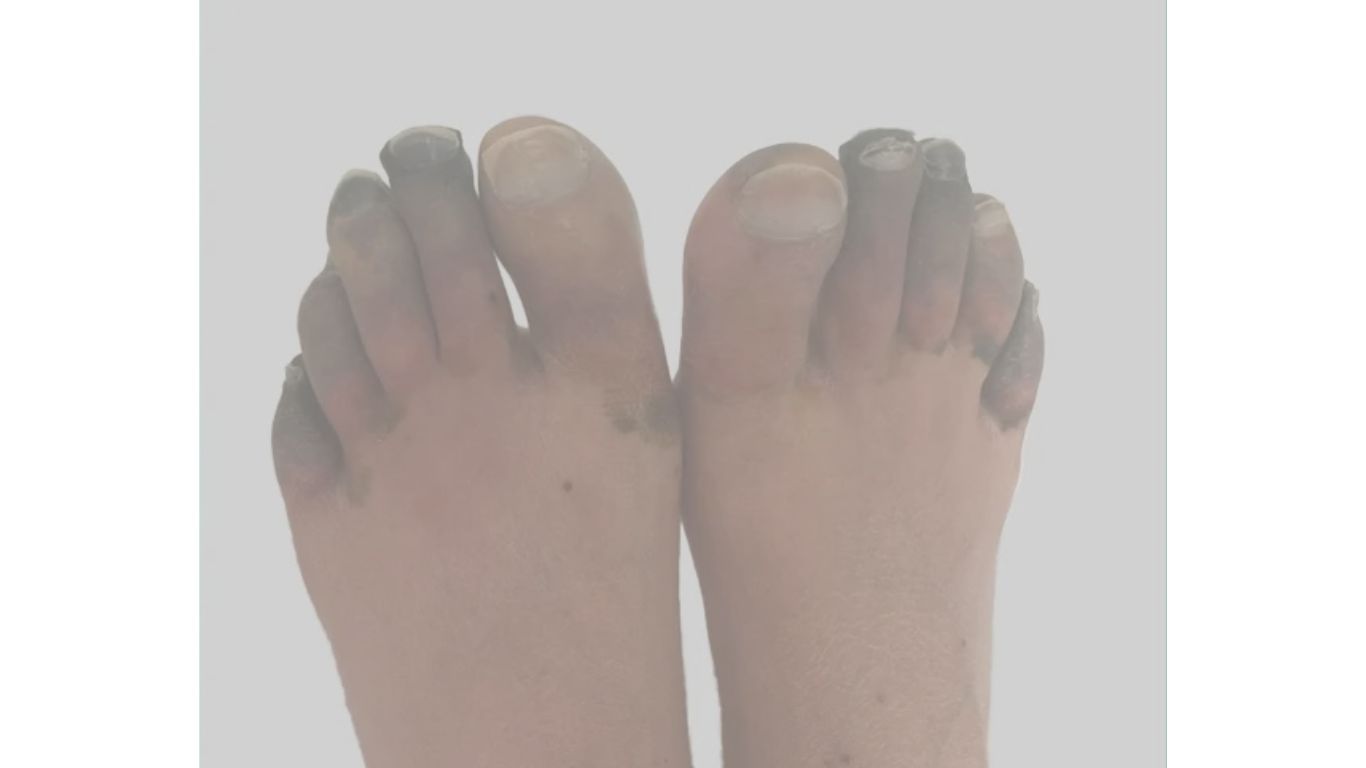
The symptoms of gangrene vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. The primary types of gangrene include dry gangrene, wet gangrene, gas gangrene, and internal gangrene. Each type has distinct signs and symptoms:
- Dry Gangrene:
- Affected area appears dry and shriveled.
- The skin changes color, progressing from pale to brown, purple, or black.
- No presence of infection, but there may be pain, numbness, or a tingling sensation.
- Typically develops slowly over time.
- Wet Gangrene:
- Affected area becomes swollen, moist, and has a foul-smelling discharge.
- The skin may blister, and the tissue turns dark or black.
- Often associated with infection and spreads rapidly.
- Gas Gangrene:
- Caused by bacterial infection, typically Clostridium species.
- Severe pain in the affected area, followed by swelling and pale skin that turns gray or purplish-red.
- Presence of gas bubbles under the skin, producing a crackling sound (crepitus) when touched.
- Fever, rapid heartbeat, and signs of septic shock may accompany the condition.
- Internal Gangrene:
- Occurs when blood flow to internal organs is blocked.
- Symptoms depend on the affected organ, such as severe abdominal pain, fever, or nausea for intestinal gangrene.
- Can lead to systemic infection and organ failure.
Causes of Gangrene
Gangrene develops when blood flow to a particular area of the body is interrupted or compromised, resulting in tissue death. Several factors can lead to this condition:
- Reduced Blood Supply (Ischemia):
- Atherosclerosis or narrowing of the arteries.
- Blood clots that obstruct circulation.
- Infection:
- Bacterial infections, particularly with Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, or Clostridium species.
- Diabetes-related foot ulcers and wounds that become infected.
- Trauma or Injury:
- Severe injuries, burns, or frostbite that damage tissues and blood vessels.
- Crush injuries causing extensive tissue damage.
- Chronic Medical Conditions:
- Diabetes, peripheral arterial disease, and other conditions that impair circulation.
- Immunosuppression, making the body more prone to infections.
- Surgery or Medical Procedures:
- Rarely, gangrene can result from surgical complications if blood flow to the tissue is unintentionally compromised.
Effects of Gangrene
The consequences of gangrene depend on its severity, location, and how quickly it is diagnosed and treated. Some of the major effects include:
- Localized Tissue Damage:
- Loss of the affected limb or part due to irreversible tissue death.
- Systemic Infection (Sepsis):
- Infection can spread throughout the body, leading to sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
- Organ Dysfunction:
- Internal gangrene can cause failure of the affected organ, such as the intestines, gallbladder, or appendix.
- Psychological Impact:
- Amputation or disfigurement can lead to emotional distress, depression, and anxiety.
- Mortality:
- If untreated, gangrene can result in death due to overwhelming infection or organ failure.
Prevention of Gangrene
Preventing gangrene involves managing risk factors, maintaining good health, and taking precautions to avoid injury and infection. Key preventive measures include:
- Control Underlying Medical Conditions:
- Manage diabetes, high blood pressure, and cholesterol to maintain healthy blood circulation.
- Regularly monitor blood sugar levels if diabetic.
- Maintain Good Hygiene:
- Clean and dress wounds promptly to prevent infection.
- Inspect the feet regularly for cuts, sores, or ulcers, especially if you have diabetes.
- Quit Smoking:
- Smoking damages blood vessels and impairs circulation, increasing the risk of gangrene.
- Exercise Regularly:
- Engage in physical activities to promote good blood flow and overall health.
- Protect Against Frostbite and Injuries:
- Dress appropriately in cold weather to prevent frostbite.
- Wear protective gear during activities that pose a risk of injury.
- Seek Prompt Medical Attention:
- Consult a doctor immediately if you notice signs of infection, poor circulation, or persistent pain in the extremities.
Homeopathic Medicines for Gangrene
Homeopathy offers supportive treatment for gangrene by addressing the underlying causes, enhancing circulation, and stimulating the body’s natural healing mechanisms. However, it is crucial to consult a qualified homeopathic practitioner for personalized treatment. Some commonly used homeopathic remedies for gangrene include:
- Arsenicum Album:
- Indicated for gangrene with burning pain, blackened tissue, and a foul-smelling discharge.
- Beneficial for individuals who feel extreme weakness and restlessness.
- Secale Cornutum:
- Used for dry gangrene, especially in elderly individuals with poor circulation.
- Symptoms include cold, shriveled, and discolored extremities.
- Carbo Vegetabilis:
- Effective for gangrene in patients with a history of poor oxygenation and sluggish circulation.
- Indicated for symptoms like cold extremities, pallor, and collapse.
- Lachesis:
- Prescribed for gangrene with bluish-black discoloration and severe pain.
- Suitable for cases where infection and sepsis are present.
- Anthracinum:
- Used for gangrenous ulcers with severe pain and foul-smelling pus.
- Beneficial in treating abscesses prone to tissue death.
- Silicea:
- Promotes the expulsion of pus and helps in the healing of infected wounds.
- Suitable for cases with delayed healing and poor immunity.
- Hepar Sulphur:
- Indicated for gangrene with signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, and pus formation.
- Helps reduce pain and inflammation.
- Calendula:
- Used topically in diluted form to clean wounds and promote healing.
- Effective in preventing infection and enhancing tissue repair.
Note: Homeopathic treatment should be used as a complementary approach alongside conventional medical care. Severe cases of gangrene often require urgent medical intervention, including antibiotics, surgery, or hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
FAQs About Homeopathic Medicines for Gangrene
1. Can homeopathy be used to treat gangrene?
Yes, homeopathy can be used as a complementary approach in the management of gangrene. Homeopathic remedies focus on enhancing the body’s natural healing processes and may help improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and alleviate symptoms. However, gangrene is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention, and homeopathy should only be used alongside conventional treatments under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
2. What are the commonly used homeopathic remedies for gangrene?
Some homeopathic remedies that are commonly considered for gangrene include:
- Arsenicum Album: For burning pain, restlessness, and discoloration of the affected area.
- Secale Cornutum: Often used for dry gangrene, especially in diabetic patients.
- Carbo Vegetabilis: For individuals with bluish skin, poor circulation, and severe weakness.
- Anthracinum: For gangrenous tissue with offensive discharges.
- Silicea: For aiding in the expulsion of dead tissue.
These remedies should only be taken after consulting a qualified homeopath, as the choice of remedy depends on the individual’s symptoms and overall health.
3. Can homeopathy prevent the progression of gangrene?
Homeopathy may help slow the progression of gangrene by improving blood flow, reducing tissue damage, and boosting the immune system. However, gangrene is a life-threatening condition, and prompt surgical or medical intervention is often necessary to prevent further complications.
4. Are homeopathic remedies safe for gangrene patients?
Homeopathic remedies are generally safe and have minimal side effects when taken under the supervision of a trained homeopath. However, relying solely on homeopathy for gangrene without seeking conventional medical treatment can lead to serious complications, including limb amputation or death.
5. How does homeopathy complement conventional treatment for gangrene?
Homeopathy can be used as an adjunct to conventional treatment by:
- Enhancing wound healing.
- Supporting the immune system.
- Managing pain and discomfort.
- Improving overall vitality and circulation.
It is important to work with both a conventional doctor and a homeopath to ensure a holistic approach to treatment.
6. Can homeopathy cure gangrene completely?
Homeopathy alone is unlikely to cure gangrene completely, especially in severe cases. It is most effective when used as a complementary therapy to support the healing process and manage symptoms. Early diagnosis and appropriate medical or surgical intervention are crucial for successful treatment.
7. How long does it take for homeopathic treatment to show results in gangrene?
The effectiveness and timeframe for results vary based on the severity of the condition, the individual’s overall health, and the remedy prescribed. Homeopathy focuses on stimulating the body’s healing mechanisms, so improvement may take time. Immediate medical care should not be delayed for homeopathic treatment.
8. Is it safe to use homeopathy alongside antibiotics or other conventional medications for gangrene?
Yes, homeopathic remedies can generally be used alongside antibiotics and other conventional medications. However, always inform your healthcare providers about all treatments you are using to avoid potential interactions and ensure coordinated care.
9. Are there any dietary or lifestyle changes recommended during homeopathic treatment for gangrene?
Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle can support the effectiveness of homeopathic treatment. Recommendations include:
- Maintaining proper hygiene to prevent infection.
- Following a balanced diet to boost immunity and promote healing.
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption to improve circulation.
- Engaging in light physical activity, as advised by your doctor, to enhance blood flow.
10. When should I consult a doctor for gangrene instead of relying on homeopathy?
Gangrene is a medical emergency. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms such as:
- Sudden discoloration of the skin (blue, black, or green).
- Severe pain or numbness in the affected area.
- Foul-smelling discharge from a wound.
- Fever or signs of infection.
Homeopathy can be considered as a supportive therapy after stabilization under a doctor’s care.
Conclusion
Gangrene is a serious condition that demands prompt medical attention to prevent complications and save lives. Awareness of its symptoms, causes, and risk factors is essential for early detection and effective treatment. By adopting healthy lifestyle practices, managing underlying conditions, and seeking timely care, the risk of gangrene can be significantly reduced. While homeopathic medicines may offer supportive care, they should not replace conventional treatments in severe cases. Collaborative management involving healthcare professionals and homeopathic practitioners can provide the best outcomes for individuals at risk of or affected by gangrene.