Discover effective homeopathic remedies for rheumatic fevers to alleviate symptoms and promote recovery from this inflammatory condition.
Introduction
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can develop as a complication of inadequately treated streptococcal throat infection, commonly known as strep throat. It primarily affects children between the ages of 5 and 15, though it can occur in adults as well. Rheumatic fever is of particular concern because it can cause long-term damage to the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The condition is most well-known for its potential to lead to rheumatic heart disease, which involves permanent damage to the heart valves.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, effects, prevention strategies, and homeopathic remedies for rheumatic fever is crucial for managing this condition effectively and preventing its long-term complications.
What Is Rheumatic Fever?
Rheumatic fever is an autoimmune inflammatory response to a streptococcal infection, particularly Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacterium responsible for strep throat and scarlet fever. When the body’s immune system fights off the streptococcal bacteria, it can mistakenly target the body’s own tissues, particularly those of the heart, joints, skin, and nervous system. This inappropriate immune response leads to the symptoms and complications associated with rheumatic fever.
The disease was much more common in the past, but with the advent of antibiotics and better public health measures, its incidence has significantly decreased in developed countries. However, rheumatic fever remains a major public health concern in many developing countries, where access to healthcare and antibiotics may be limited.
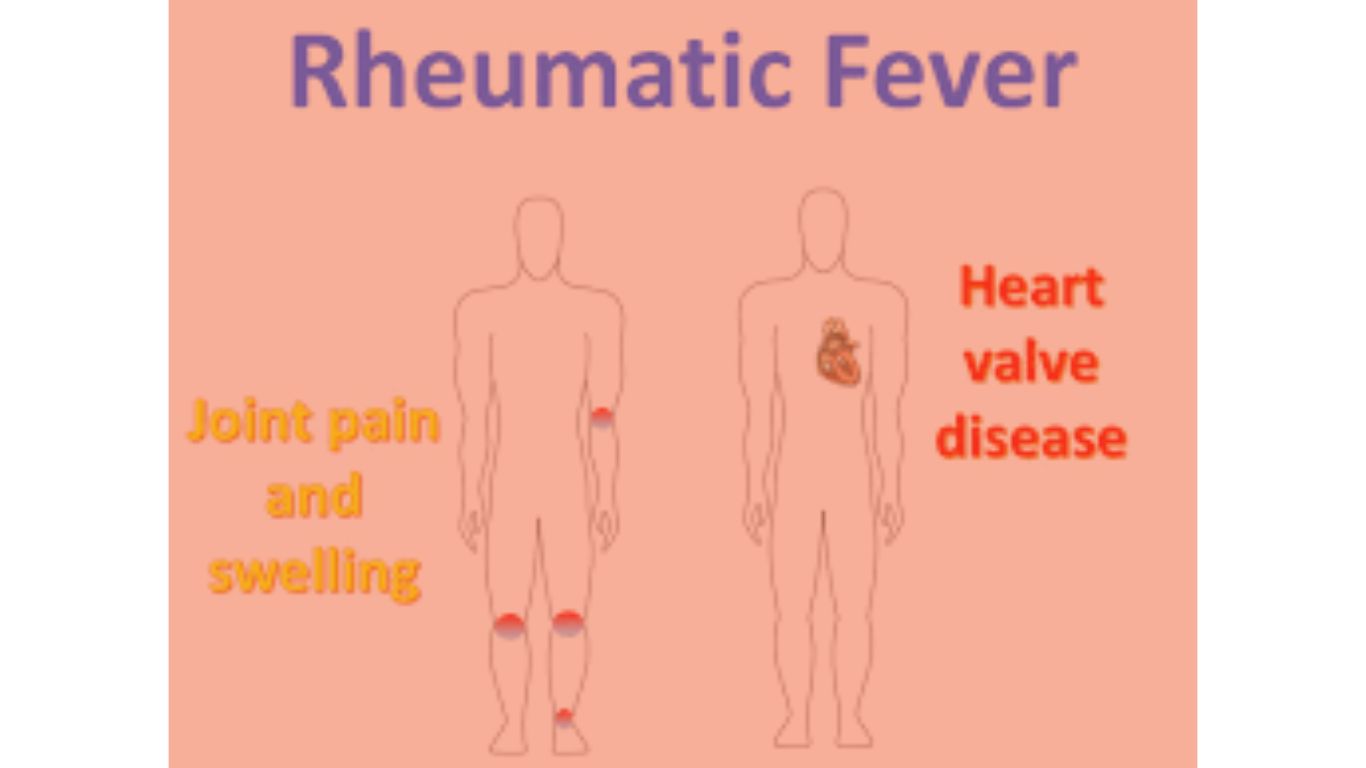
Symptoms of Rheumatic Fever
The symptoms of rheumatic fever typically develop 1 to 5 weeks after a strep throat infection. The presentation of symptoms can vary widely from person to person, and not everyone with rheumatic fever will experience all of the symptoms. The major symptoms include:
- Fever:
- A high temperature is one of the first signs of rheumatic fever. The fever can range from mild to high and is often accompanied by other symptoms such as chills and sweating.
- Painful and Swollen Joints:
- Polyarthritis, or inflammation of multiple joints, is a hallmark of rheumatic fever. The large joints, such as the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists, are most commonly affected. The joints may become red, swollen, and extremely painful to touch or move. The inflammation typically migrates from one joint to another, a phenomenon known as “migratory arthritis.”
- Carditis:
- Inflammation of the heart, or carditis, occurs in about half of all rheumatic fever cases. This inflammation can affect the heart’s outer lining (pericardium), the inner lining (endocardium), or the muscle itself (myocardium). Symptoms of carditis include chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, and fatigue. Carditis can lead to permanent damage to the heart valves, a condition known as rheumatic heart disease.
- Sydenham’s Chorea:
- Also known as St. Vitus’ dance, Sydenham’s chorea is a neurological disorder characterized by rapid, uncoordinated jerking movements, particularly in the face, hands, and feet. The movements are involuntary and may be accompanied by emotional instability, such as crying or laughing inappropriately. Sydenham’s chorea typically occurs several months after the initial strep infection.
- Erythema Marginatum:
- Erythema marginatum is a distinctive rash that appears as pink or red rings or crescents with clear centers. The rash usually appears on the trunk or limbs and is not itchy or painful. It tends to worsen with heat and may fade and reappear over time.
- Subcutaneous Nodules:
- These are small, painless lumps that develop under the skin, usually over the bony areas of the joints, such as the elbows, knees, and wrists. Subcutaneous nodules are a less common symptom of rheumatic fever and are typically associated with severe carditis.
- Other Symptoms:
- Other symptoms of rheumatic fever may include fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss, abdominal pain, and nosebleeds.
The severity of rheumatic fever can vary, with some individuals experiencing only mild symptoms, while others may develop severe complications that can lead to long-term health problems.
Causes of Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever is a delayed autoimmune response to an infection with group A streptococcus bacteria. The pathogenesis of rheumatic fever involves several steps:
- Strep Throat Infection:
- The initial cause of rheumatic fever is a streptococcal throat infection, commonly known as strep throat. The bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes is responsible for this infection, which is characterized by symptoms such as sore throat, fever, red and swollen tonsils, and white patches on the throat.
- Immune Response:
- When the body detects the presence of streptococcal bacteria, the immune system mounts a response to eliminate the pathogen. Antibodies are produced to target specific proteins on the surface of the bacteria.
- Molecular Mimicry:
- A phenomenon known as molecular mimicry occurs when the antibodies produced against the streptococcal bacteria mistakenly recognize and attack similar proteins in the body’s own tissues. In the case of rheumatic fever, these antibodies primarily target the tissues of the heart, joints, skin, and brain.
- Inflammation:
- The immune system’s attack on the body’s own tissues leads to inflammation, which is responsible for the symptoms of rheumatic fever. The inflammation can be widespread, affecting multiple organs and systems.
- Genetic Predisposition:
- Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing rheumatic fever. Certain genetic markers have been associated with an increased risk of developing the disease after a streptococcal infection.
It is important to note that not everyone who has a strep throat infection will develop rheumatic fever. The condition typically occurs in individuals who have had repeated strep infections or who have not received adequate treatment for their initial infection.
Effects of Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever can have serious and lasting effects on the body, particularly if not treated promptly and effectively. The potential effects of rheumatic fever include:
- Rheumatic Heart Disease:
- Rheumatic heart disease is the most serious complication of rheumatic fever and occurs when the inflammation caused by the disease damages the heart valves. The mitral valve, which separates the left atrium and left ventricle, is most commonly affected, but other valves may also be involved. The damage to the heart valves can lead to conditions such as mitral stenosis (narrowing of the valve), mitral regurgitation (leakage of the valve), and heart failure. Rheumatic heart disease can result in long-term disability and may require surgical intervention, such as valve repair or replacement.
- Chronic Arthritis:
- Although the joint inflammation associated with rheumatic fever typically resolves without long-term damage, some individuals may develop chronic arthritis, particularly if they experience recurrent episodes of rheumatic fever.
- Chronic Fatigue:
- Individuals who have experienced rheumatic fever may continue to suffer from chronic fatigue and weakness, even after the acute phase of the disease has resolved.
- Neurological Complications:
- Sydenham’s chorea, the neurological manifestation of rheumatic fever, can persist for several months and may lead to long-term motor and emotional disturbances. In rare cases, Sydenham’s chorea can recur years later.
- Recurrent Rheumatic Fever:
- Individuals who have had rheumatic fever are at risk of developing recurrent episodes if they are exposed to streptococcal bacteria again. Each recurrence increases the risk of further damage to the heart and other organs.
- Psychosocial Impact:
- The chronic nature of rheumatic fever and its complications can have a significant psychosocial impact, particularly in children and adolescents. The disease may lead to missed school days, social isolation, and emotional distress.
The long-term effects of rheumatic fever underscore the importance of early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and ongoing medical care to prevent complications.
Prevention of Rheumatic Fever
Preventing rheumatic fever involves several strategies, including the prompt and effective treatment of streptococcal infections, ongoing preventive care, and public health measures.
- Prompt Treatment of Strep Throat:
- The most effective way to prevent rheumatic fever is to promptly diagnose and treat strep throat with antibiotics. Penicillin is the most commonly prescribed antibiotic for strep throat, and it is highly effective in eliminating the streptococcal bacteria. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve, to ensure that the infection is completely eradicated.
- Preventive Antibiotic Therapy:
- Individuals who have had rheumatic fever are at high risk of developing recurrent episodes, particularly if they are exposed to streptococcal bacteria again. To prevent recurrences, long-term antibiotic prophylaxis is often recommended. This typically involves regular injections of benzathine penicillin G or oral penicillin. The duration of prophylaxis depends on several factors, including the severity of the initial rheumatic fever episode and the presence of rheumatic heart disease.
- Public Health Measures:
- Public health measures to reduce the incidence of streptococcal infections can play a significant role in preventing rheumatic fever. These measures include promoting good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, and ensuring access to healthcare services for the early diagnosis and treatment of strep throat.
- Education and Awareness:
- Educating healthcare providers, patients, and the general public about the importance of treating strep throat and the potential consequences of rheumatic fever is crucial for prevention. Increased awareness can lead to earlier diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and better outcomes.
- Vaccination:
- While there is currently no vaccine available specifically for preventing rheumatic fever, research is ongoing to develop a streptococcal vaccine that could prevent the initial infection and, consequently, rheumatic fever.
Effective Homeopathic Remedies for Rheumatic Fevers
Homeopathy offers a range of remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms of rheumatic fever and support the body’s natural healing processes. It is important to note that homeopathic treatment for rheumatic fever should be individualized, and consultation with a qualified homeopathic practitioner is recommended. The following are some commonly used homeopathic remedies for rheumatic fever:
- Belladonna:
- Indications: Belladonna is often indicated in the early stages of rheumatic fever when there is sudden onset of high fever, intense heat, and throbbing pain in the affected joints. The person may have a flushed face, dilated pupils, and sensitivity to light and noise.
- Key Symptoms: High fever, red face, throbbing pain, and sensitivity to stimuli.
- Bryonia alba:
- Indications: Bryonia is useful for rheumatic fever with slow onset of symptoms, particularly when there is severe pain in the joints that worsens with movement. The person may be irritable and prefer to lie still, with a strong desire for cold drinks.
- Key Symptoms: Slow onset of symptoms, pain worsened by movement, and irritability.
- Rhus toxicodendron:
- Indications: Rhus tox is commonly used for rheumatic fever with joint stiffness and pain that is relieved by movement. The person may experience restlessness, especially at night, and feel worse in cold, damp weather.
- Key Symptoms: Joint stiffness, restlessness, and relief with movement.
- Arsenicum album:
- Indications: Arsenicum album is indicated for rheumatic fever with severe fatigue, restlessness, and anxiety. The person may experience burning pain in the joints, which is relieved by warmth, and may have a strong desire for small sips of water.
- Key Symptoms: Fatigue, restlessness, burning pain, and anxiety.
- Causticum:
- Indications: Causticum is used for rheumatic fever with muscle weakness and contracture of tendons. The person may have difficulty moving the affected joints and may experience tearing or drawing pain. Causticum is also indicated for rheumatic heart disease with palpitations and chest pain.
- Key Symptoms: Muscle weakness, contracture, tearing pain, and heart symptoms.
- Kali bichromicum:
- Indications: Kali bichromicum is indicated for rheumatic fever with wandering joint pains that shift from one joint to another. The pain is often described as stitching or shooting, and the person may feel better with warmth.
- Key Symptoms: Wandering joint pain, stitching pain, and relief with warmth.
- Pulsatilla:
- Indications: Pulsatilla is useful for rheumatic fever with changeable symptoms and a weepy, emotional disposition. The person may have shifting joint pains, lack of thirst, and a desire for fresh air. Pulsatilla is also indicated for heart symptoms with a feeling of tightness in the chest.
- Key Symptoms: Changeable symptoms, weepiness, lack of thirst, and desire for fresh air.
- Medorrhinum:
- Indications: Medorrhinum is indicated for rheumatic fever with a history of suppressed gonorrhea or other sexually transmitted infections. The person may experience severe pain in the joints, particularly at night, and may feel better after urinating.
- Key Symptoms: History of suppressed infections, severe joint pain, and relief after urination.
- Aconitum napellus:
- Indications: Aconite is useful in the early stages of rheumatic fever when the symptoms come on suddenly after exposure to cold wind. The person may have a high fever, intense anxiety, and restlessness, with a fear of death.
- Key Symptoms: Sudden onset, high fever, anxiety, and restlessness.
- Spigelia:
- Indications: Spigelia is indicated for rheumatic fever with severe pain in the heart region, radiating to the back and left arm. The person may experience palpitations, shortness of breath, and a sensation of tightness in the chest.
- Key Symptoms: Severe heart pain, palpitations, and shortness of breath.
Homeopathic Treatment Considerations
Homeopathic treatment for rheumatic fever should be guided by a qualified practitioner who can assess the individual’s symptoms and overall constitution. The remedies mentioned above are only a few of the many that may be indicated in cases of rheumatic fever. The selection of the appropriate remedy is based on the specific symptoms and the person’s overall health and emotional state.
It is important to note that homeopathic remedies are not a substitute for conventional medical treatment in cases of severe rheumatic fever or rheumatic heart disease. Homeopathy can be used as a complementary therapy to support the body’s healing processes, but conventional treatment, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications, should not be neglected.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Effective Homeopathic Remedies for Rheumatic Fevers
1. What is rheumatic fever, and what are its primary symptoms?
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can develop after a streptococcal throat infection (strep throat). It primarily affects the heart, joints, skin, and brain. Common symptoms include fever, joint pain and swelling, chest pain, skin rash, and involuntary movements (chorea). It can also cause damage to the heart valves, leading to rheumatic heart disease.
2. How can homeopathy assist in managing rheumatic fever?
Homeopathy aims to support the body’s natural healing processes by using highly diluted substances that match the patient’s symptoms. For rheumatic fever, homeopathic remedies may help alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and support overall recovery. Homeopathic treatment is typically used alongside conventional medical care for a comprehensive approach.
3. What are some commonly used homeopathic remedies for rheumatic fever?
Some homeopathic remedies commonly used for rheumatic fever include:
- Bryonia alba: Useful for symptoms with severe joint pain that worsens with movement and improves with rest. It is also indicated for a dry cough and chest pain.
- Rhus toxicodendron: Effective for joint pain that improves with movement and warmth, and worsens with cold and damp conditions.
- Apis mellifica: Indicated for swelling and redness in the joints, with a sensation of burning and stinging.
- Kali bichromicum: Used when symptoms include joint pain with a tendency to shift from one joint to another and the presence of a specific type of rash.
- Mercurius solubilis: Useful for cases with inflamed joints, possible heart involvement, and symptoms such as profuse sweating and a foul breath.
4. Are homeopathic remedies safe for children with rheumatic fever?
Homeopathic remedies are generally considered safe for children. However, it is crucial to consult a qualified homeopathic practitioner to ensure that the remedies are appropriate for the child’s age, health condition, and specific symptoms. Homeopathic treatment should be integrated with conventional medical care for the best outcome.
5. Can homeopathic remedies be used alongside conventional treatments for rheumatic fever?
Yes, homeopathic remedies can be used alongside conventional treatments to support overall health and symptom relief. It is important to inform all healthcare providers about the use of homeopathic remedies to ensure a coordinated approach and to avoid any potential interactions.
6. How do I choose the right homeopathic remedy for rheumatic fever?
Selecting the appropriate homeopathic remedy involves considering the specific symptoms, their severity, and the individual’s overall condition. A qualified homeopathic practitioner can help determine the most suitable remedy based on a detailed assessment of the patient’s symptoms and health history.
7. How should homeopathic remedies be administered for rheumatic fever?
Homeopathic remedies are typically administered in the form of pellets, liquid drops, or tablets. The dosage and frequency depend on the specific remedy and the severity of the symptoms. It is important to follow the instructions provided by a homeopathic practitioner or on the product label.
8. Can homeopathic remedies cure rheumatic fever?
Homeopathic remedies are intended to support the body’s natural healing processes and manage symptoms. They are not a substitute for conventional medical treatments. For rheumatic fever, which can involve serious complications, it is essential to seek conventional medical care in addition to using homeopathic remedies.
9. How long does it take to see results from homeopathic remedies for rheumatic fever?
The time to see results from homeopathic remedies can vary depending on the individual, the severity of the symptoms, and the appropriateness of the chosen remedy. Some individuals may notice improvement within a few days, while others may take longer. Monitoring symptoms and consulting a practitioner if there is no improvement or if symptoms worsen is important.
10. Are there any side effects associated with homeopathic remedies for rheumatic fever?
Homeopathic remedies are generally considered safe with minimal risk of side effects due to their highly diluted nature. However, individual reactions can vary. If any adverse reactions or worsening of symptoms occur, it is important to discontinue use and consult a healthcare provider.
11. Can homeopathic remedies be used in conjunction with over-the-counter medications for rheumatic fever?
Homeopathic remedies can often be used alongside over-the-counter medications. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure that there are no interactions between the homeopathic remedies and other medications.
12. Where can I find reliable homeopathic remedies for rheumatic fever?
Reliable homeopathic remedies can be obtained from licensed homeopathic practitioners, reputable health food stores, or online pharmacies specializing in homeopathic products. Ensure that the remedies are sourced from reputable manufacturers to ensure quality and effectiveness.
13. Is it necessary to consult a homeopathic practitioner for rheumatic fever?
While some individuals may use homeopathic remedies based on general knowledge, consulting a qualified homeopathic practitioner is recommended for personalized treatment. A practitioner can provide a thorough evaluation and tailor the remedies to address the specific symptoms and needs of the individual.
14. What should I do if homeopathic remedies do not seem to work for rheumatic fever?
If homeopathic remedies do not provide relief or if symptoms worsen, it is important to seek conventional medical care. Homeopathy can be a complementary approach, but serious conditions like rheumatic fever require appropriate medical treatment.
15. Can homeopathy be used to prevent rheumatic fever?
Homeopathy can offer preventive remedies based on individual susceptibility and symptom profiles. For preventive care, it is best to consult a homeopathic practitioner who can recommend appropriate remedies and strategies tailored to the individual’s health and risk factors. It is also important to address strep throat infections promptly with conventional medical care to prevent rheumatic fever.
Conclusion
Rheumatic fever is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that can have long-term consequences if not treated promptly and effectively. Understanding the symptoms, causes, effects, and prevention strategies for rheumatic fever is crucial for managing the disease and preventing its complications.
Homeopathy offers a range of remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms of rheumatic fever and support the body’s natural healing processes. However, it is important to approach homeopathic treatment with care and to seek professional medical advice when necessary.
By taking a proactive approach to the prevention and treatment of rheumatic fever, individuals can protect their health and well-being and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Whether through conventional medicine, homeopathy, or a combination of both, managing rheumatic fever effectively requires a holistic approach that addresses both the symptoms and the underlying causes of the disease.