Table of Contents
TogglePhysometra-Symptoms, Causes, and Homeopathic Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
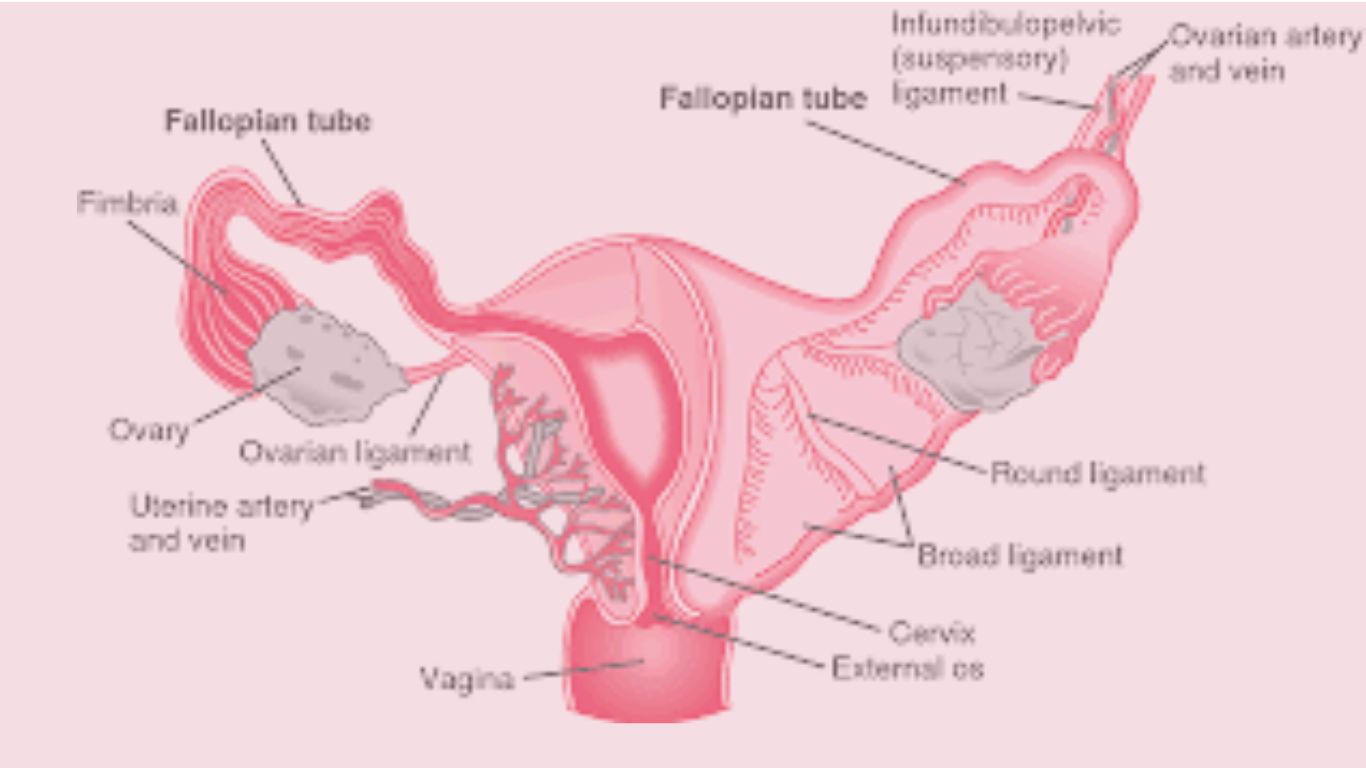
Physometra, a condition characterized by the presence of gas or air within the uterine cavity, is a relatively uncommon but significant gynecological concern. While conventional medicine often addresses it with procedures like cervical dilation or antibiotics for any underlying infection, homeopathy offers a holistic, individualized approach. This system of medicine aims not just to suppress the symptom of uterine gas but to correct the underlying energetic disturbance and susceptibility that allowed the condition to manifest. It views physometra not as an isolated disease but as a local expression of a systemic internal imbalance.
This article delves into the homeopathic perspective on physometra, exploring the best-indicated medicines, their characteristic symptoms, potencies, uses, and the philosophy behind their selection. It is crucial to remember that the information presented here is for educational purposes, and self-prescription for such a condition is strongly discouraged. Consulting a qualified homeopathic practitioner is essential for safe and effective treatment.
Understanding Physometra and Its Symptom Picture
In homeopathic terms, physometra is seen as a result of a vital force imbalance, often linked to factors like uterine atony (lack of muscle tone), septic absorption, or the presence of gas-forming bacteria following childbirth, miscarriage, or surgical procedures like D&C. The symptoms a woman experiences are the guideposts for selecting the correct remedy.
The key symptoms can include:
-
A sensation of fullness, distension, or pressure in the pelvic region.
-
Cramping or bearing-down pain in the uterus.
-
The passage of foul-smelling, gaseous, or bloody vaginal discharge.
-
General weakness and fatigue.
-
Symptoms may worsen with movement or pressure and might be associated with emotional states like anxiety or grief.
A homeopath will conduct a detailed interview to understand physometra causes and the complete symptom picture, including the patient’s mental and emotional state, food cravings, thermal modalities (whether the person feels better or worse with heat or cold), and any peculiar or characteristic sensations.
Leading Homeopathic Medicines for Physometra
Several homeopathic remedies have an affinity for the female reproductive system and cover the symptom complex of physometra. The choice depends entirely on the individual’s unique presentation.
1. Sepia Officinalis (Ink of the Cuttlefish)
Sepia is often considered a top contender for a wide range of uterine ailments, including physometra, especially when it arises from uterine prolapse or atony.
-
Characteristic Symptoms:
-
A pronounced bearing-down sensation in the pelvis, as if everything would protrude through the vulva. The patient may feel the need to cross her legs or sit tightly.
-
Sensation of a ball or plug in the inner parts.
-
Leucorrhea (vaginal discharge) that is yellow-greenish, and often profuse and offensive.
-
Indifference and irritability: A key mental symptom is a sense of indifference towards one’s family and loved ones, coupled with irritability and a desire to be left alone.
-
Worse from: Cold air, dampness, before thunderstorms, and in the evening.
-
Better from: Warmth, vigorous exercise, and pressure.
-
-
Causes and Uses: Sepia is profoundly useful for physometra following childbirth, especially when associated with uterine subinvolution (failure to return to normal size). It is also indicated for issues stemming from hormonal imbalances, like those seen during menopause.
-
Potencies: Both low (6C, 30C) and high potencies (200C, 1M) are used. Lower potencies are often repeated, while higher potencies are reserved for a deeper, constitutional prescription by an experienced practitioner.
2. Lachesis Muta (Bushmaster Snake Venom)
Lachesis is a premier remedy for conditions with a strong septic element, intense congestion, and a left-sided affinity. It is invaluable for severe, acute cases of physometra with signs of infection.
-
Characteristic Symptoms:
-
Extreme sensitivity to touch and pressure. The patient cannot bear anything tight around the abdomen or waist.
-
A feeling of constriction in the uterine region.
-
Offensive, discolored (often dark) discharge that may be acrid and cause smarting.
-
Aggravation from sleep: Symptoms are markedly worse upon waking. The patient feels much worse after sleeping.
-
Mental State: Loquacity, jealousy, suspicion, and a feeling of being controlled or dominated.
-
-
Causes and Uses: Lachesis is critical in post-abortal or puerperal (post-childbirth) physometra where there is a high risk of sepsis. It addresses the intense inflammation and toxicity associated with such states.
-
Potencies: Medium to high potencies (30C, 200C) are commonly used in acute, serious conditions, but should only be administered under professional supervision.
3. Pyrogenium (Artificial Sepsin)
When physometra is a direct result of septic infection, Pyrogenium is a life-saving remedy. It is the homeopathic answer to sepsis, acting as a powerful antidote to the toxins produced by bacteria.
-
Characteristic Symptoms:
-
Profuse, horribly offensive, brownish discharge. The odor is so foul that it is unforgettable.
-
A profound discrepancy between pulse and temperature. For instance, a rapid pulse with a relatively low temperature, or vice-versa.
-
Intense, aching, and bruised feeling all over the body, as if lying on a hard bed.
-
Restlessness and a feeling of being terribly ill.
-
-
Causes and Uses: Pyrogenium is the go-to remedy for septicemic states, post-surgical infections, and infected abortions leading to physometra. It helps the body overcome the systemic toxicity.
-
Potencies: Typically used in higher potencies (200C, 1M) in acute, critical situations.
4. Pulsatilla Nigricans (Wind Flower)
Pulsatilla is a quintessential women’s remedy, characterized by mildness, changeability, and a thirstless state. It is suited for gentle, yielding women whose symptoms are constantly shifting.
-
Characteristic Symptoms:
-
Thick, bland, creamy yellow or greenish discharge that changes in its color and consistency.
-
Bearing-down pain, as if the uterus were being dragged down.
-
Weepiness and a desire for consolation. The patient feels better when someone shows them sympathy and attention.
-
All symptoms are changeable, and pains tend to wander from one part to another.
-
Worse from: Heat, warm rooms, in the evening.
-
Better from: Cool, open air, gentle motion, and sympathy.
-
-
Causes and Uses: Pulsatilla is excellent for physometra following suppressed menstruation or after childbirth, especially in women who fit the gentle, emotional Pulsatilla constitution.
-
Potencies: Commonly used in 30C or 200C potencies.
5. Kreosotum (Beechwood Kreosote)
Kreosotum is indicated when the discharge is extremely acrid, corrosive, and causes intense irritation and swelling of the vulva.
-
Characteristic Symptoms:
-
Burning, acrid, offensive leucorrhea that stains linen yellow and causes intense itching and smarting.
-
The discharge is worse between menstrual periods and after urinating.
-
A feeling of prostration and heaviness in the uterine region.
-
The patient may feel very irritable and cross.
-
-
Causes and Uses: It is particularly useful when the corrosive nature of the discharge is the most prominent feature, leading to soreness and swelling of the external genitals.
-
Potencies: 6C to 30C are frequently employed.
Potency and Dosage: A Delicate Art
The selection of potency in homeopathy is as important as the selection of the remedy itself. It is not a case of “one size fits all.”
-
Low Potencies (6X, 6C, 30C): These are often used for local, physical symptoms and are typically repeated more frequently (e.g., 2-3 times a day). They are considered safer for self-administration in minor acute issues but are still not recommended for a condition like physometra without guidance.
-
Medium and High Potencies (200C, 1M, 10M): These are used for deeper-seated, chronic, or constitutional issues. They act on the mental and emotional planes and the vital force more profoundly. A single dose of a high potency can have a long-lasting effect and should only be prescribed by a qualified homeopath after a thorough case analysis.
For physometra, which often has an acute presentation on a chronic susceptible background, a practitioner might start with a medium potency like 200C as a single dose and wait for a response, or use a low potency more frequently to manage acute pain and discharge.
Side Effects and the Homeopathic Aggravation
Homeopathic medicines, being highly diluted, are generally free from toxic chemical side effects. However, a phenomenon known as a “homeopathic aggravation” can occur. This is a temporary intensification of existing symptoms, which is seen as a positive sign that the vital force has been stimulated and is beginning to react. This aggravation is usually short-lived and is followed by a marked improvement in the overall condition.
To minimize the risk of an aggravation, the correct remedy must be matched to the symptom picture with the minimal necessary dose. This is another critical reason to seek professional guidance, as an incorrect remedy will simply have no effect.
Prevention and Holistic Management
Homeopathy’s goal is not only to cure the existing ailment but also to strengthen the constitution to prevent recurrence. A well-chosen constitutional remedy can improve uterine tone, hormonal balance, and overall vitality.
Alongside homeopathic treatment, supportive measures are vital:
-
Hygiene: Maintaining proper perineal hygiene, especially after childbirth or surgery.
-
Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in iron, vitamins, and minerals to support healing and immune function.
-
Rest: Adequate physical rest is crucial for recovery from any condition affecting the pelvic organs.
-
Managing Emotional Stress: Since emotional shocks and chronic stress can be underlying causes, counseling, meditation, or other stress-management techniques can be beneficial.
Comparative Analysis with Other Remedies
To further clarify the selection process, here is a brief comparison:
-
Sepia vs. Lilium Tigrinum: Both have a bearing-down sensation. However, Sepia has indifference and irritability, and feels better with vigorous exercise. Lilium tig has a constant bearing-down with a sensation of a ball in the rectum; the patient feels a compelling need to support the perineum and is often in a great hurry, with a sense of cardiac anxiety.
-
Lachesis vs. Pyrogenium: Both are for septic conditions. Lachesis has intense loquacity, left-sided symptoms, and aggravation from sleep. Pyrogenium’s keynote is the horrible offensiveness of all discharges and the pulse-temperature discrepancy. Lachesis is more about congestion and toxicity, while Pyrogenium is about frank sepsis and prostration.
-
Pulsatilla vs. Kreosotum: Both can have leucorrhea. Pulsatilla’s discharge is bland, thick, and changeable, with a weepy, consolable temperament. Kreosotum’s discharge is intensely acrid, burning, and offensive, causing great irritation, with an irritable, cross mental state.
In conclusion, homeopathy provides a sophisticated and deeply individualized framework for treating physometra. By looking beyond the local pathology to the entire person—her physical sensations, emotional landscape, and unique modalities—a homeopath can select a remedy that resonates with her vital force, stimulating a true and lasting healing response. While the remedies discussed here are powerful tools, their power is unlocked only through the skilled art and science of homeopathic prescription. Therefore, any woman suspecting she has physometra should first seek a conventional diagnosis and then, if she chooses, consult a professionally trained homeopathic practitioner for complementary care.
Frequently Asked Questions about Homeopathy for Physometra
Q1: Can homeopathy really cure physometra, or does it just manage the symptoms?
Homeopathy aims for a curative response. The philosophy is to stimulate the body’s own self-healing mechanisms to address the root cause of the condition. In the case of physometra, a well-selected homeopathic remedy does not just expel the gas or mask the pain. It works by correcting the underlying functional disturbance, such as uterine atony (weakness) or the body’s susceptibility to infection, which led to the accumulation of gas in the first place. By strengthening the vital force, homeopathy seeks to resolve the current episode and reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
Q2: How do I know which homeopathic medicine is right for my case of physometra?
This is the most critical step and the core of homeopathic practice. The selection is not based on the disease name “physometra” but on your unique, individual symptom picture. A homeopath will look for the most characteristic and peculiar symptoms. For instance:
-
If you have a strong bearing-down sensation and feel indifferent to your family, Sepia might be considered.
-
If the discharge is horribly offensive and you feel deeply septic and bruised, Pyrogenium could be the remedy.
-
If you are weepy, crave consolation, and your symptoms are constantly changing, Pulsatilla may be indicated.
Consulting a qualified homeopath is essential because they are trained to take this detailed case and differentiate between similar remedies.
Q3: Is it safe to self-prescribe a homeopathic medicine for physometra?
It is strongly discouraged. While homeopathic medicines are non-toxic, selecting the wrong remedy will result in no improvement, wasting valuable time during which the condition could worsen. Physometra can sometimes be a sign of a serious underlying issue, such as a severe infection or tissue trauma, which requires a conventional medical diagnosis and monitoring. Self-prescription for such a specific gynecological condition carries a risk of misunderstanding the symptoms and delaying necessary care. A professional homeopath can also manage the treatment within the context of your overall health.
Q4: What are the side effects of homeopathic medicines for this condition?
Homeopathic medicines, due to their high dilution, do not have chemical side effects like conventional drugs. However, there is a process known as a “homeopathic aggravation.” This is a temporary, mild intensification of your existing symptoms that can occur after taking the correct remedy. It is seen as a positive sign that the body’s healing energy has been powerfully activated. This aggravation is short-lived and is typically followed by a significant improvement in your overall condition. An incorrect remedy will produce no such effect or change.
Q5: What potency should I start with, and how often should I take the medicine?
Potency and dosage are highly individualized and best determined by a practitioner. However, to give a general idea:
-
For acute, painful symptoms, lower potencies like 6C or 30C may be used, often repeated several times a day.
-
For a deeper-acting, constitutional effect, or in cases with a strong septic element, a single dose of a higher potency like 200C or 1M may be prescribed.
The frequency of dosage is not standardized; it depends on the acuity of your symptoms and your body’s response. The fundamental rule is to stop repeating the dose as soon as improvement begins.
Q6: Can I use homeopathy alongside antibiotics or other conventional treatments for physometra?
Yes, in many cases, homeopathy can be used as a complementary therapy. It is crucial, however, to keep all your healthcare providers informed. A homeopath and your medical doctor can work in tandem. Homeopathy may help improve your overall vitality, support the body’s response to infection, and promote healing of the uterine tissues, potentially enhancing the effects of conventional care. There are no known drug interactions, but a holistic view of your treatment plan is best.
Q7: How long does it take to see results with homeopathic treatment for physometra?
The time frame for improvement varies greatly. In an acute, recent case, where the correct remedy is matched perfectly, you might feel relief from pain and a reduction in discharge within hours or a few days. For a more chronic condition, or one that has been present for a longer time, it may take longer to see significant change. The speed of recovery is influenced by your overall health, the severity of the condition, and the accuracy of the homeopathic prescription.
Q8: Will homeopathic treatment prevent physometra from happening again?
This is a key goal of constitutional homeopathic treatment. By addressing the underlying susceptibility—such as a tendency toward uterine weakness, poor recovery after childbirth, or a predisposition to infections—homeopathy aims to strengthen your system fundamentally. A course of well-chosen constitutional remedies can improve the tone and health of the reproductive organs, making you less likely to develop conditions like physometra in the future. This preventive aspect is a cornerstone of classical homeopathy.