Discover effective homeopathic remedies for tachycardia. Explore natural solutions to normalize heart rate and well-being for patients seeking alternative treatment options.
Tachycardia refers to a condition in which the heart rate exceeds the normal resting rate, typically defined as a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute in adults. While a fast heartbeat is normal during exercise or in response to stress, tachycardia can be a cause for concern when it occurs at rest or without an obvious trigger. This condition can range from being a benign issue to a serious medical problem that requires immediate attention. Understanding the symptoms, causes, effects, prevention strategies, and homeopathic remedies for tachycardia is essential for managing this condition effectively.
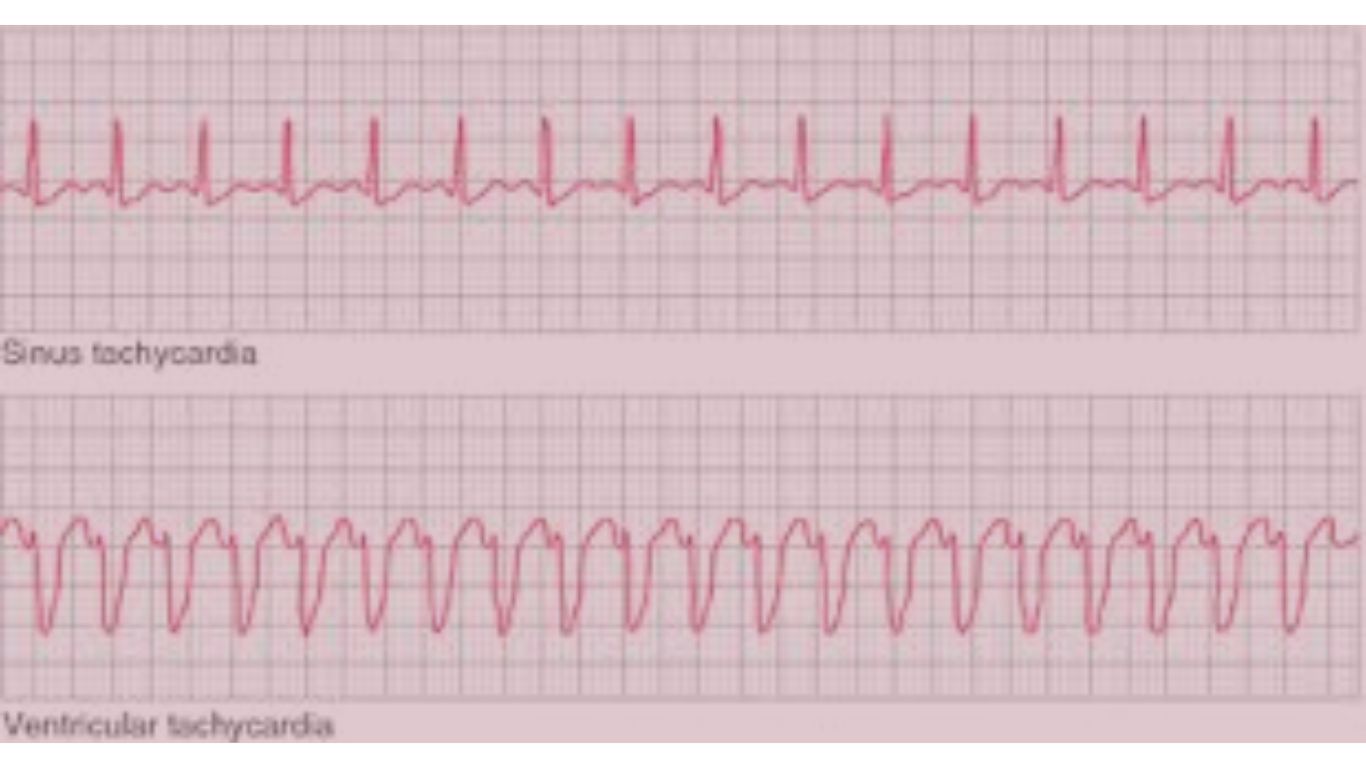
Understanding Tachycardia
Tachycardia is a broad term that encompasses various types of fast heartbeats. The condition can be classified based on its origin within the heart and the underlying cause. The three main types of tachycardia are:
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): This type of tachycardia originates above the ventricles (in the atria or AV node). It often presents as a sudden onset of a fast heartbeat and can be triggered by stress, caffeine, or certain medications.
- Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): Originating in the ventricles (the heart’s lower chambers), VT is often more serious than SVT and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. VT is commonly associated with heart disease and can lead to complications such as ventricular fibrillation, a condition that can cause sudden cardiac arrest.
- Sinus Tachycardia: This type occurs when the sinus node, which is the natural pacemaker of the heart, sends out electrical signals at a faster-than-normal rate. Sinus tachycardia can be a normal response to exercise, fever, or stress, but when it occurs at rest, it may indicate an underlying health issue.
Symptoms of Tachycardia
The symptoms of tachycardia can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, as well as the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Rapid Heartbeat: The most noticeable symptom of tachycardia is a fast or racing heartbeat, often felt as a pounding or fluttering sensation in the chest. The heart rate may exceed 100 beats per minute, even at rest.
- Palpitations: Individuals with tachycardia may experience palpitations, which are the sensations of the heart beating irregularly or forcefully. These palpitations can be unsettling and may cause anxiety.
- Shortness of Breath: As the heart beats faster, it may struggle to supply enough oxygenated blood to the body, leading to shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, particularly during physical activity or at rest.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: A rapid heartbeat can reduce blood flow to the brain, causing symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or a feeling of faintness.
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: Tachycardia can cause chest pain or discomfort, particularly if the heart is working harder than usual to pump blood. This symptom may be more pronounced in individuals with underlying heart disease.
- Fatigue: Persistent tachycardia can lead to fatigue, as the heart is overworked and unable to pump blood efficiently. This can result in a general feeling of tiredness and lack of energy.
- Syncope (Fainting): In severe cases, tachycardia can cause fainting or near-fainting episodes, particularly if the heart is unable to maintain adequate blood pressure and circulation.
- Anxiety or Panic: The sudden onset of a fast heartbeat can trigger feelings of anxiety or panic, particularly if the individual is unsure of the cause. This can create a cycle where anxiety exacerbates the tachycardia.
Causes of Tachycardia
Tachycardia can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from lifestyle choices to underlying medical conditions. Identifying the cause is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Cardiac Causes
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms, or arrhythmias, are a common cause of tachycardia. These can occur due to issues with the heart’s electrical system, leading to irregular or fast heartbeats.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): A common type of arrhythmia where the heart’s upper chambers (atria) beat irregularly, leading to a rapid and irregular heartbeat.
- Atrial Flutter: Similar to AFib, but with a more regular rhythm, atrial flutter can cause the heart to beat very fast.
- Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): A serious arrhythmia that originates in the ventricles and can lead to life-threatening conditions such as ventricular fibrillation.
- Heart Disease: Tachycardia can be a symptom of various forms of heart disease, including coronary artery disease (CAD), heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and valvular heart disease.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Some individuals are born with structural heart abnormalities that can predispose them to tachycardia.
- Previous Heart Attack: Damage to the heart muscle from a previous heart attack can lead to scarring and changes in the heart’s electrical pathways, resulting in tachycardia.
- High Blood Pressure: Chronic high blood pressure can strain the heart and lead to the development of tachycardia over time.
- Heart Surgery: Individuals who have undergone heart surgery may be at increased risk of developing tachycardia due to changes in the heart’s structure and function.
Non-Cardiac Causes
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress, anxiety, and panic attacks can trigger sinus tachycardia, where the heart rate increases as part of the body’s “fight or flight” response.
- Stimulants: The consumption of stimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, and certain drugs (e.g., amphetamines, cocaine) can lead to tachycardia by increasing the heart rate and blood pressure.
- Medications: Certain medications, including some decongestants, asthma inhalers, and thyroid medications, can cause tachycardia as a side effect.
- Thyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormone, can cause the heart to beat faster, leading to tachycardia.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Imbalances in electrolytes such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium can disrupt the heart’s electrical signals, leading to tachycardia.
- Fever: An elevated body temperature due to infection or illness can cause the heart to beat faster as the body tries to maintain homeostasis.
- Anemia: Low levels of hemoglobin or red blood cells can reduce oxygen delivery to tissues, prompting the heart to beat faster to compensate, leading to tachycardia.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can lead to dehydration, causing the heart to beat faster to maintain blood pressure and circulation.
- Physical Exertion: Intense exercise or physical exertion can cause a temporary increase in heart rate, which may develop into tachycardia if the body is not adequately conditioned.
- Alcohol and Drug Use: Excessive alcohol consumption and the use of certain recreational drugs can trigger episodes of tachycardia.
Effects of Tachycardia
The effects of tachycardia on the body can range from mild discomfort to serious, life-threatening complications, depending on the underlying cause and the duration of the condition.
- Decreased Cardiac Efficiency: When the heart beats too quickly, it may not have enough time to fill properly between beats. This can lead to decreased cardiac output, meaning the heart is less efficient at pumping blood to the rest of the body.
- Reduced Oxygen Supply: Tachycardia can reduce the amount of oxygen-rich blood reaching the body’s tissues and organs. This can result in symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
- Increased Risk of Stroke: In conditions like atrial fibrillation, the rapid and irregular heartbeat can cause blood to pool in the heart’s atria, increasing the risk of blood clots. If a clot travels to the brain, it can cause a stroke.
- Heart Failure: Prolonged or recurrent tachycardia can weaken the heart muscle over time, leading to heart failure. In heart failure, the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, resulting in symptoms such as swelling, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
- Sudden Cardiac Arrest: In severe cases, particularly with ventricular tachycardia, the condition can lead to ventricular fibrillation—a life-threatening arrhythmia that can cause sudden cardiac arrest. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate intervention.
- Emotional and Psychological Impact: The experience of tachycardia can be distressing, leading to anxiety, panic attacks, and a reduced quality of life. The fear of experiencing tachycardia may cause individuals to avoid certain activities or situations, leading to social withdrawal.
- Impaired Physical Activity: Tachycardia can limit a person’s ability to engage in physical activity due to symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness, and fatigue. This can result in decreased physical fitness and overall health.
- Sleep Disturbances: Tachycardia that occurs at night can disrupt sleep, leading to insomnia, daytime fatigue, and irritability. Sleep deprivation can further exacerbate the condition.
Prevention of Tachycardia
Preventing tachycardia involves addressing the underlying causes, making lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, using medical interventions. Here are some strategies to prevent tachycardia:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Manage Stress: Stress and anxiety are significant triggers for tachycardia. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or progressive muscle relaxation. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and engaging in hobbies can also help manage stress.
- Limit Stimulants: Reduce or eliminate the intake of stimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, and certain medications that can increase heart rate. Be cautious with energy drinks and other products that contain high levels of caffeine.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can trigger tachycardia. Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels, or avoid it altogether if it is a known trigger.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight can strain the heart and increase the risk of tachycardia. Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can lead to tachycardia, so it’s important to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially during hot weather or physical activity.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular exercise strengthens the heart and improves cardiovascular fitness, which can help prevent tachycardia. However, it’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity of exercise, particularly if you are out of shape or have a history of heart problems.
- Avoid Recreational Drugs: The use of recreational drugs such as cocaine and amphetamines can trigger tachycardia and other serious heart conditions. Avoiding these substances is crucial for heart health.
- Monitor Heart Rate: If you are prone to tachycardia, monitor your heart rate regularly, especially during physical activity. Knowing your normal heart rate range can help you identify when something is wrong.
Medical Interventions
- Medication Management: If you are taking medications that can cause tachycardia as a side effect, talk to your healthcare provider about possible alternatives or adjustments.
- Treat Underlying Conditions: Managing conditions such as hyperthyroidism, anemia, or electrolyte imbalances is essential in preventing tachycardia. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for treating these conditions.
- Cardiac Procedures: In some cases, procedures such as catheter ablation may be necessary to correct the electrical pathways in the heart that are causing tachycardia. This procedure involves destroying small areas of heart tissue that are causing abnormal heart rhythms.
- Pacemaker or ICD: For individuals with recurrent or life-threatening tachycardia, a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) may be recommended. These devices help regulate the heart’s rhythm and can deliver shocks if necessary to restore a normal heartbeat.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help monitor heart health and detect any early signs of tachycardia or other heart conditions. Early intervention is key to preventing complications.
Homeopathic Remedies for Tachycardia
Homeopathy offers a natural and individualized approach to treating tachycardia. The choice of remedy depends on the specific symptoms, the underlying cause, and the patient’s overall constitution. Here are some commonly used homeopathic remedies for tachycardia:
1. Aconitum Napellus (Aconite)
- Indications: Aconite is often recommended for tachycardia that arises suddenly, particularly after a shock, fright, or anxiety. The person may feel an intense fear of death or impending doom.
- Symptoms: Rapid, forceful heartbeat with restlessness, fear, and anxiety. Tachycardia may be accompanied by cold sweat and a sensation of tightness in the chest.
- Dosage: Aconite is typically prescribed in low potencies (6X or 30C), with dosage depending on the severity and frequency of symptoms.
2. Arsenicum Album
- Indications: Arsenicum Album is useful for tachycardia associated with anxiety, especially at night. The person may be very restless and feel a need to move around despite being weak.
- Symptoms: Irregular heartbeat, often with a sensation of weakness and exhaustion. Tachycardia may be accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest and difficulty breathing.
- Dosage: Commonly used in potencies of 6C to 30C, depending on the individual’s sensitivity and symptom severity.
3. Nux Vomica
- Indications: Nux Vomica is suited for individuals who experience tachycardia due to overwork, stress, or stimulant use (e.g., caffeine, alcohol).
- Symptoms: Tachycardia is often accompanied by irritability, digestive disturbances, and a feeling of heaviness in the chest. The person may be highly sensitive to noise, light, and other stimuli.
- Dosage: Nux Vomica is often prescribed in low to medium potencies (6C to 30C), taken in the evening or before bedtime.
4. Ignatia Amara
- Indications: Ignatia is recommended for tachycardia that occurs as a result of emotional stress, particularly grief, disappointment, or suppressed emotions.
- Symptoms: The person may experience a sensation of a lump in the throat, sighing, or a sensation of emptiness in the chest. Tachycardia may occur after emotional outbursts or during periods of intense stress.
- Dosage: Typically used in potencies of 6C to 30C, depending on the emotional state and symptom intensity.
5. Lachesis Mutus
- Indications: Lachesis is useful for tachycardia that worsens at night or during sleep. It is also indicated for individuals who feel a sensation of suffocation or tightness in the chest.
- Symptoms: The person may feel better after discharging emotions (e.g., crying) and worse when lying down. Tachycardia may be accompanied by hot flashes, particularly in women going through menopause.
- Dosage: Usually prescribed in low to medium potencies (6C to 30C), taken as needed to manage symptoms.
6. Coffea Cruda
- Indications: Coffea Cruda is indicated for tachycardia that results from excitement, joy, or excessive intake of caffeine. It is particularly useful for individuals who are sensitive to stimulants.
- Symptoms: The person may experience a rapid, fluttering heartbeat, often accompanied by restlessness, insomnia, and heightened sensitivity to stimuli.
- Dosage: Coffea Cruda is typically used in low potencies (6C to 30C), taken at the onset of symptoms.
7. Spigelia Anthelmia
- Indications: Spigelia is recommended for tachycardia associated with sharp, stabbing chest pain that may radiate to the neck or arms.
- Symptoms: The heartbeat may be irregular or excessively rapid, and tachycardia may be triggered by physical exertion or emotional stress. The person may feel worse when lying on the left side.
- Dosage: Spigelia is commonly used in low to medium potencies (6C to 30C), depending on the intensity of symptoms.
8. Digitalis Purpurea
- Indications: Digitalis is suited for tachycardia associated with a slow, weak, or irregular heartbeat, particularly in individuals with heart disease or a history of heart issues.
- Symptoms: The person may experience a sensation of the heart stopping or skipping beats, followed by a strong thump. Tachycardia may be accompanied by a feeling of tightness in the chest and difficulty breathing.
- Dosage: Digitalis is typically prescribed in low potencies (6C to 30C), with careful monitoring of symptoms.
FAQs About Homeopathic Remedies for Tachycardia
1. What is tachycardia, and how can homeopathy help?
Answer: Tachycardia is a condition characterized by an abnormally rapid heart rate, typically defined as a resting heart rate above 100 beats per minute. It can be caused by various factors, including stress, fever, or heart conditions. Homeopathy aims to address the root causes and symptoms of tachycardia by using highly diluted remedies that stimulate the body’s natural healing abilities. A homeopath will choose remedies based on individual symptoms, emotional state, and overall health to help restore normal heart rhythm and reduce symptoms.
2. What are some common homeopathic remedies for tachycardia?
Answer: Several homeopathic remedies are used for tachycardia, depending on the specific symptoms and underlying causes. Common remedies include:
- Aconitum Napellus: Often used for tachycardia that occurs suddenly after a shock, fright, or anxiety.
- Digitalis Purpurea: Helpful for tachycardia accompanied by a slow, irregular heartbeat and symptoms of heart weakness.
- Cactus Grandiflorus: Used for tachycardia with a feeling of constriction in the chest and palpitations that worsen at night.
- Crataegus Oxyacantha: Known for its use in improving cardiac function and addressing symptoms of heart disease, including tachycardia.
3. How do I determine the right homeopathic remedy for my tachycardia?
Answer: Determining the right homeopathic remedy involves a detailed assessment of your symptoms, emotional state, and overall health. A qualified homeopath will consider factors such as the frequency and triggers of tachycardia, any associated symptoms (e.g., anxiety, chest pain), and your general health condition. Based on this information, they will select a remedy that matches your specific symptom profile and health needs.
4. Are homeopathic remedies safe for treating tachycardia?
Answer: Homeopathic remedies are generally considered safe due to their highly diluted nature, which minimizes the risk of side effects. However, it is important to use homeopathy as a complementary approach rather than a replacement for conventional medical treatments. If you experience persistent or severe tachycardia, consult with a healthcare provider to address any underlying health conditions and ensure that homeopathic remedies are used appropriately.
5. How long does it take for homeopathic remedies to show results for tachycardia?
Answer: The time it takes for homeopathic remedies to show results can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the tachycardia. Some people may notice improvements within a few days, while others may take several weeks to experience significant changes. Regular follow-up with a homeopath is important to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
6. Can homeopathic remedies be used alongside conventional treatments for tachycardia?
Answer: Yes, homeopathic remedies can often be used alongside conventional treatments for tachycardia, provided they are used under the guidance of both a homeopath and a healthcare provider. It is important to inform all your healthcare practitioners about any complementary treatments you are using to ensure they are compatible and to avoid potential interactions.
7. What lifestyle changes can support homeopathic treatment for tachycardia?
Answer: Lifestyle changes can complement homeopathic treatment for tachycardia and promote overall heart health. Recommended changes include:
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress and anxiety.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid excessive consumption of stimulants like caffeine and alcohol.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to support cardiovascular health and manage stress.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get sufficient rest each night to support overall health and well-being.
8. Where can I find a qualified homeopath to treat my tachycardia?
Answer: To find a qualified homeopath, you can start by searching for professional homeopathic associations or organizations that maintain directories of certified practitioners. You can also ask for recommendations from friends, family, or your healthcare provider. It is important to choose a homeopath who is licensed and experienced in treating conditions similar to yours.
9. Can homeopathy cure tachycardia completely?
Answer: Homeopathy aims to address the underlying causes of tachycardia and support overall heart health. While many individuals experience significant relief from symptoms, the effectiveness of homeopathy can vary based on individual factors, including the severity of the condition and overall health. It is important to work with a qualified homeopath and follow a comprehensive approach that includes conventional medical care and lifestyle modifications as needed.
Conclusion
Tachycardia is a condition that can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life and, in some cases, can lead to serious health complications. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and effects of tachycardia, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage this condition effectively. Lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and homeopathic remedies all play a role in addressing tachycardia and promoting heart health. As always, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action based on the individual’s specific circumstances.